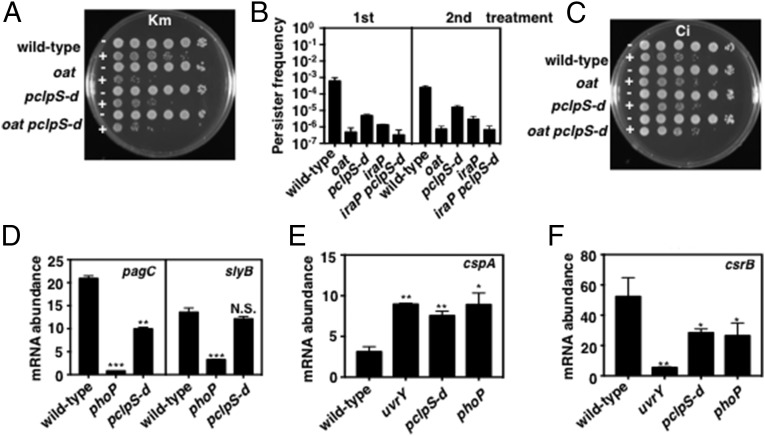
Fig. 5.
PhoP-dependent stabilization of ClpS clients increases antibiotic persistence and alters gene expression. (A) Kanamycin persister bacteria by wild-type (14028s), oat (JY903), pclpS-d (JY665), and oat pclpS-d (JY981) Salmonella following growth in N-minimal medium (pH 7.7) containing 10 μM MgCl2 at 37 °C for 6 h and incubation with kanamycin (Km) (100 μg/mL) for 2 h. Shown are 10-fold serial dilutions plated on LB agar plates. (B) Frequency of kanamycin persister bacterial exhibited by wild-type (14028s), oat (JY903), pclpS-d (JY665), iraP (EG17133), and iraP pclpS-d (JY936) Salmonella was determined by the number of colonies on LB agar plates after treatment with kanamycin (100 μg/mL) for 2 h. The second treatment shows persister formation by the colonies recovered from the LB agar plates following the first treatment and subjected to the same treatment. Data shown are the mean and SD from two independent experiments. (C) As in A, but cells were treated with ciprofloxacin (Ci) (2 μg/mL). (D) mRNA abundance of the pagC and slyB genes produced by wild-type (14028s), phoP (MS7953s), and pclpS-d (JY665) Salmonella following growth in in N-minimal medium (pH 7.7) containing 10 μM MgCl2 at 37 °C for 5.5 h. (E and F) mRNA abundance of the cspA (E) and csrB (F) genes produced by wild-type (14028s), uvrY (JY917), pclpS-d (JY665), and phoP (MS7953s) Salmonella following growth in in N-minimal medium (pH 7.7) containing 10 μM MgCl2 at 37 °C for 5.5 h. For D–F, mRNA abundance was normalized to that of the ompA gene. Primers used in qRT-PCR are listed in Table S2. Data shown are the mean and SD from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, two-tailed t test with each sample vs. wild-type.