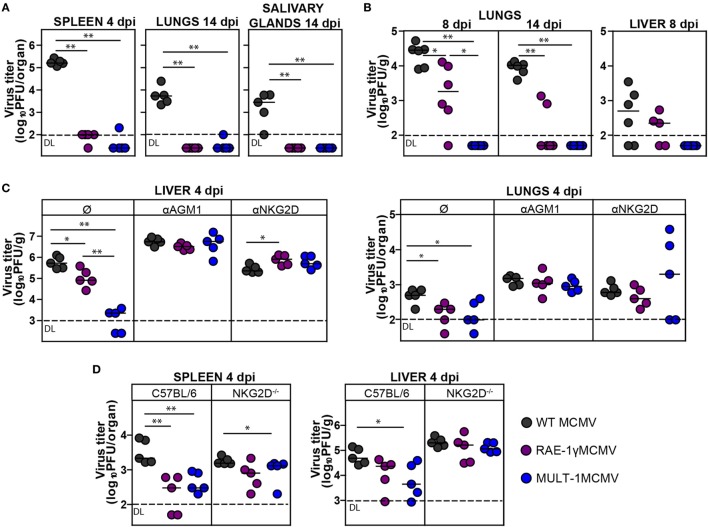
Figure 2.
Recombinant murine CMV (MCMV) expressing MULT-1 is controlled by NK cells in NKG2D-dependent manner. (A) BALB/c mice were infected intravenously (i.v.) with 2 × 105 PFU of wild-type (WT) MCMV, RAE-1γMCMV, and MULT-1MCMV. On day 4 and 14 after infection viral titer was determined in organs by plaque assay. (B) Newborn C57BL/6 mice were infected with 200 PFU of WT MCMV, RAE-1γMCMV, and MULT-1MCMV intraperitoneally (i.p.) 24 h after birth. Viral titer was determined in organs by plaque assay on day 8 and 14 after infection. (C) BALB/c mice received 20 µl of αAGM1 or 250 µg of NKG2D blocking antibody i.p. 2 h before infection and additional dose of NKG2D blocking antibody on day 2 after i.v. infection with 2 × 105 PFU of WT MCMV, RAE-1γMCMV, and MULT-1MCMV. Viral titer was determined in organs by plaque assay on day 4 after infection. (D) C57BL/6 and NKG2D−/− mice were i.v. infected with 5 × 105 PFU of WT MCMV, RAE-1γMCMV, and MULT-1MCMV. On day 4 after infection viral titer was determined in organs by plaque assay. Each circle represents an individual animal and lines represent medians. Data were analyzed using Mann–Whitney U test. Asterisks denote significant values: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. Abbreviation: DL, detection limit.