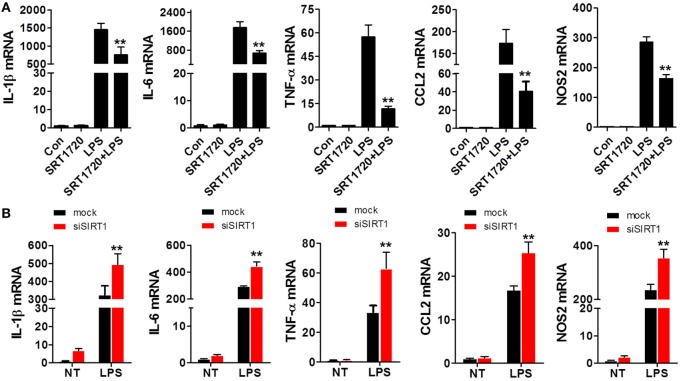
Figure 2.
SIRT1 activation and inhibition led, respectively, to a decrease and increase in pro-inflammatory cytokines in macrophages. (A) RAW264.7 cells were treated with PBS (control) or SRT1720 or with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or LPS + SRT1720, and then RT-PCR was performed to assess the expression levels of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, NOS2, and CCL2. **p < 0.01 compared with the LPS group; n = 6. (B) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with SIRT1 siRNA or mock siRNA and then the knockdown and control cells were treated with LPS or PBS (NT). The expression levels of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, NOS2, and CCL2 were examined using RT-PCR. **p < 0.01 compared with the LPS + mock group; n = 6.