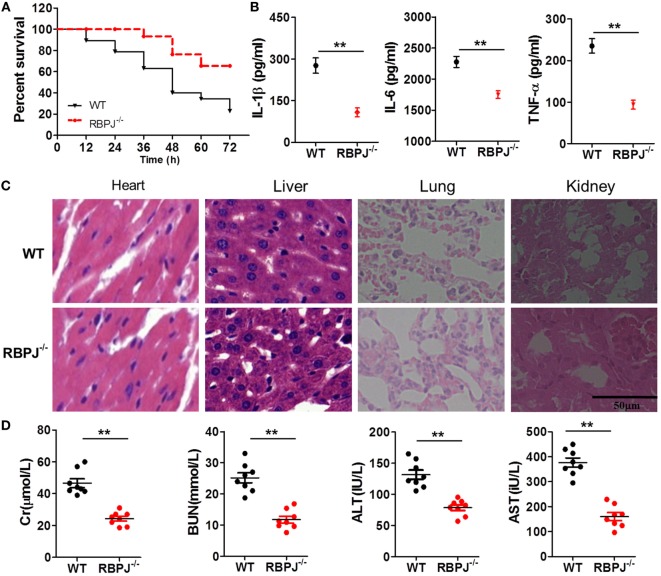
Figure 8.
RBP-J knockout resulted in decreased inflammation in vivo. (A) Survival rates of wild-type (WT) and RBP-J−/− mice after 72-h stimulation with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). (B) IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α levels in blood were measured using a microplate reader. (C) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of heart, liver, lung, and kidney tissues from RBP-J−/− and WT mice after peritoneal injection of LPS. Sections were examined and photographed under a microscope. (D) Levels of creatinine (Cr), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and aspartate transaminase (AST) in blood were determined using commercial ELISA kits. **p < 0.01 compared with WT mice; n = 6. Scale bar = 50 µm.