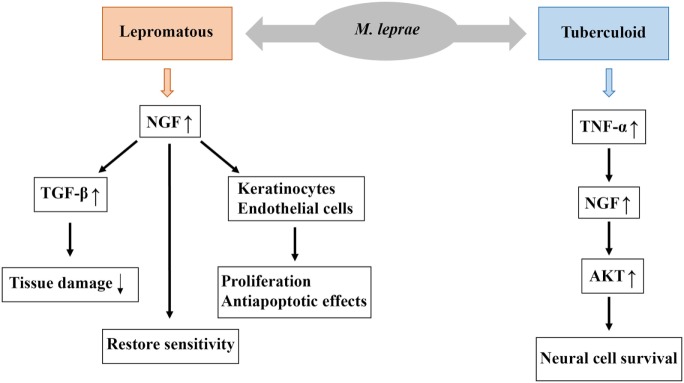
Figure 3.
Possible biological role of nerve growth factor (NGF) in the pathogenesis of leprosy. Higher levels of NGF are associated with lepromatous forms, and this increased NGF expression stimulates the expression of TGF-β, which reduce tissue damage resulting from nerve injury. Moreover, NGF restore sensitivity and exerts proliferative and antiapoptotic effects on keratinocytes and endothelial cells. Low levels of NGF are associated with tuberculoid forms and this low expression of NGF stimulates the expression of TNF-α which may contribute to the evolution of neural lesions. Low levels of NGF may also contribute to the development of neuropathy, such as sensitivity loss, nerve demyelination, and degeneration.