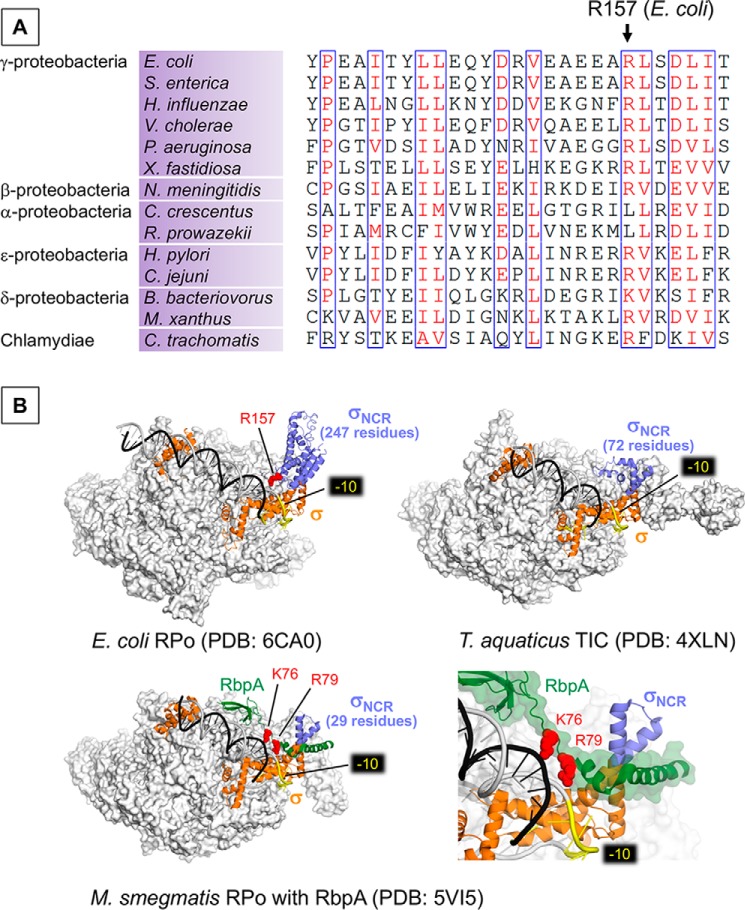
Figure 4.
A, alignment of the σNCR region shows the conservation of Arg-157 residue in bacteria from the classes of proteobacteria and Chlamydiae. B, the structures of E. coli RPo (top left), Thermus aquaticus RPo (top right), and Mycobacterium smegmatis (RPo with RbpA, bottom) as transparent surface models with corresponding σ factors (orange) and promoter DNA (t-DNA, dark gray; nt-DNA, light gray) shown as ribbon models. σNCR is in purple and RbpA of M. smegmatis RPo (bottom) is in green. −10 elements are colored yellow. Positively charged residues interacting with bases upstream to −10 promoter elements (Arg-157 of E. coli σNCR, Arg-79 and Lys-76 of RbpA) are shown as sphere model (red). Right bottom panel is a magnified view showing the RbpA and DNA interaction.