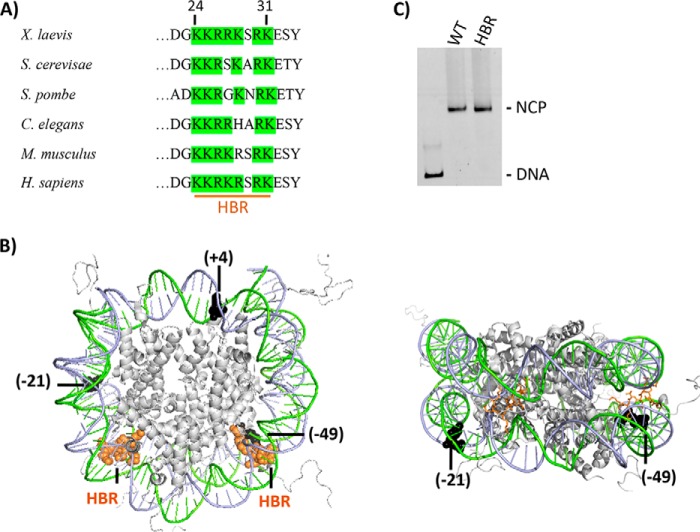
Figure 1.
The HBR domain in histone H2B. A, HBR sequence alignment from various species was adapted from Parra et al. (27). As can be seen, the HBR domain (e.g. residues 24–31 in X. laevis, 30–37 in S. cerevisiae, and 27–37 in Homo sapiens) is highly conserved among species and is predominantly comprised of positively charged amino acids (50, 51). B, in the left figure, PDB code 1KX5 was modified to highlight the structural location of the HBR domain (orange spheres) relative to BER lesions (black spheres). A different view with the HBR domain displayed as sticks is shown on the right. For the lesions (uracil or single-nucleotide gap), the number in parentheses indicates the number of nucleotides away from the pseudo 2-fold axis of symmetry called the dyad, toward the 5′ end (+) or (−) toward the 3′ end of the damaged strand. All lesions are inwardly oriented or occluded, with their phosphate backbone facing the histone octamer. Lesions at −49 and +4 located in the I strand (green) and −21 in the J strand (blue). C, representative 6% native gel illustrating reconstitution efficiency of DNA with recombinant X. laevis WT and HBR (Δ24–31) octamers.