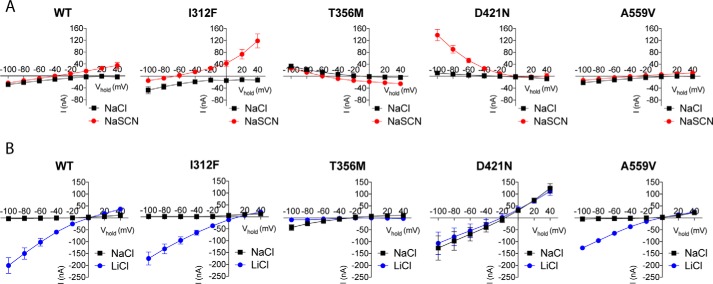
Figure 4.
Functionally impaired DAT variants display gain-of-function electrophysiological properties. A, dopamine-induced currents through indicated DAT variants. I/V recordings were made in NaCl, and in NaSCN to isolate the uncoupled anion conductance. For I312F, Cl− substitution to SCN generates a greater left-shift in reversal potential and a larger outward current at positive potentials, compared with DAT WT, which is consistent with an enhanced uncoupled anion conductance. T356M and seemingly also D421N conduct an aberrant dopamine-associated outward current at negative potentials, which is markedly enhanced in NaSCN for D421N. B, leak conductances were evaluated by recording cocaine-sensitive currents (Icontrol − Icocaine) in NaCl and LiCl. Both T356M and D421N show enhanced leak conductances in NaCl. For D421N, the leak conductance in NaCl is similar in size and reversal potential to the leak current in LiCl. In contrast, Na+ substitution for Li+ completely abolishes the leak current through T356M, in marked contrast to DAT WT. All curves presented in A and B are mean ± S.E. from 4 to 11 experiments.