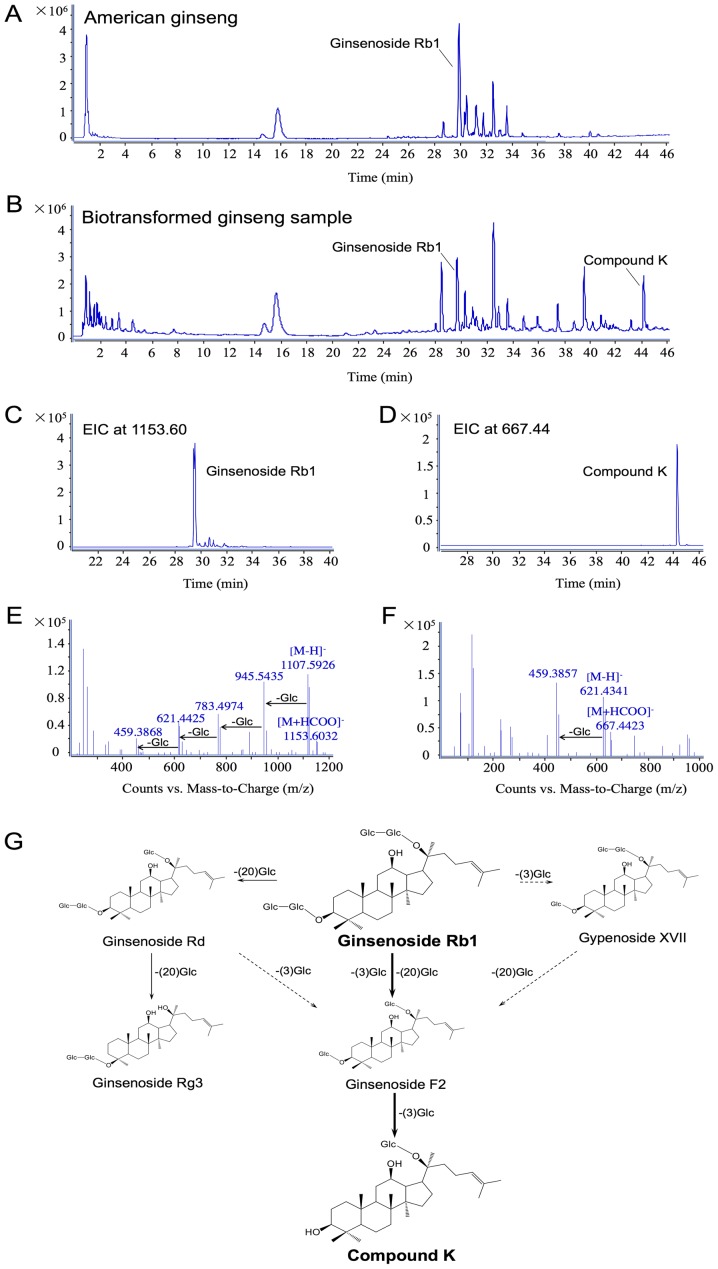
Figure 1.
Biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1 to compound K by human enteric microflora. Liquid chromatography quadruple time-of-flight-MS data are shown in (A-F). (A) Total ion chromatography of American ginseng extract, in which Rb1 occupies the highest peak. (B) TIC of biotransformed American ginseng sample, in which compound K is one of the identified main metabolites. (C) EIC of Rb1 in biotransformed sample with a narrow window of 0.01 Da. (D) EIC of compound K with a narrow window of 0.01 Da. (E) MS/MS spectra of Rb1, and (F) MS/MS spectra of compound K. (G) Proposed metabolic pathways via gut microflora from Rb1 to compound K. EIC, extracted ion chromatogram; MS, mass spectrometry; TIC, total ion chromatography.