Figure 1.
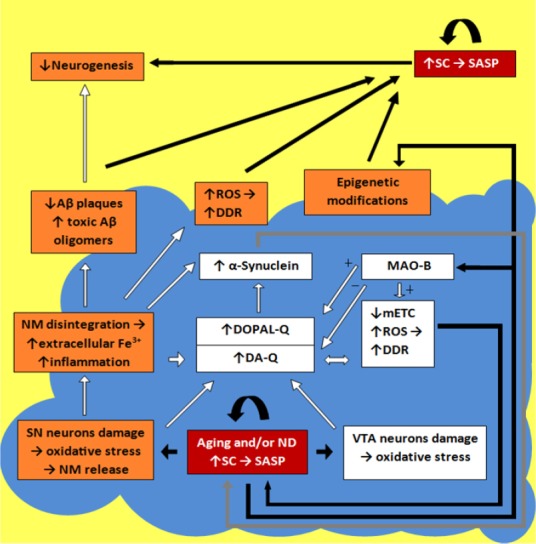
Schematic imaging of pathways and factors transforming dopaminergic cells into their senescent forms in aging and/or neurodegeneration (ND).
Blue fragment is the DA-producing areas (SN and VTA) in the brain (open boxes mark factors functioning inside these areas); red boxes mark areas where cells are transformed into their senescent forms; orange boxes mark the main critical factors involved in the cell senescence (the boxes, overlapping the blue-yellow border, mark the factors usable on each side). The details of the senescence pathways functioning are described in the text. SC: Senescent cells; DA-Q: dopamine-quinone; DOPAL-Q: 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde-quinone; DDR: damage DNA response; Aβ: amyloid-beta; MAO-B: monoamine oxidase B; NM: neuromelanin; mETC: mitochondrial electron transport chain; ROS: reactive oxygen species; SASP: senescence-associated secretory phenotype; SN: substantia nigra; VTA: ventral tegmental area.
