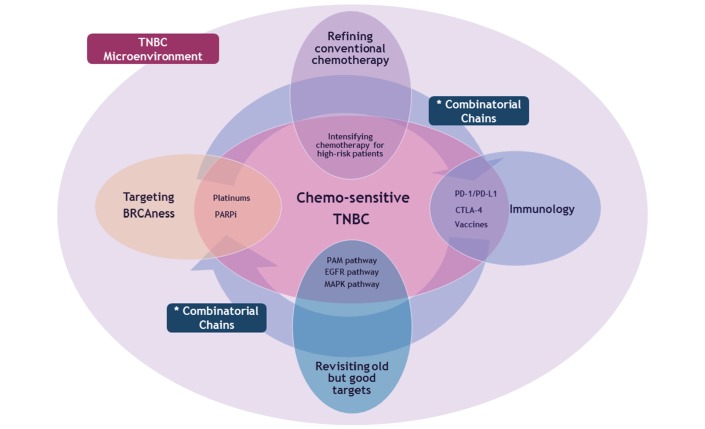
Figure 2.
Future aspects of therapeutic strategies in patients with TNBC based on its chemosensitivity and immune-molecular heterogeneity. Future challenge in TNBC is fundamentally to enrich the therapeutic efficacy to the optimal level both for chemosensitive and chemoresistant population. In this context, conventional chemotherapy and these four key entities constitute the main domain of upcoming treatment strategies. Targeting the BRCAness, revisiting our old but competent targets including PAM pathway and emerging immunotherapy can be the master molecular regulators of TNBC tumour microenvironment. Smart refining of conventional chemotherapy should be accompanied with these molecular targeting. Finally, combinatorial chains between these four independent domains would be the key of future therapeutics for TNBC. CTLA-4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; PAM, PI3K-Akt-mTOR; PARPi, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors; PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1, programmed cell death ligand 1; TNBC, triple-negative breast cancer.