Table 1. Optimization of reaction conditions a .
| |||||
| Entry | Cu salt | Oxidant | Additive (eq.) | Solvent | Yield (%) b |
| 1 | Cu(OAc)2 | K2CO3 (2) | 1,4-Dioxane | 0 | |
| 2 | Cu(OAc)2 | K2HPO4 (2) | 1,4-Dioxane | 0 | |
| 3 | Cu(OAc)2 | PhCO2Na (2) | 1,4-Dioxane | 0 | |
| 4 | Cu(OAc)2 | Et3N (2) | 1,4-Dioxane | <5 | |
| 5 | Cu(OAc)2 | Py (2) | 1,4-Dioxane | 22 | |
| 6 | Cu(OAc)2 | 2,6-Lutidine (2) | 1,4-Dioxane | 14 | |
| 7 | Cu(OAc)2 | DMAP (2) | 1,4-Dioxane | 17 | |
| 8 | Cu(OAc)2 | TMEDA (1) | 1,4-Dioxane | 6 | |
| 9 | Cu(OAc)2 | 2,2′-Dipyridyl (1) | 1,4-Dioxane | 16 | |
| 10 | Cu(OAc)2 | 1,10-Phen (1) | 1,4-Dioxane | <5 | |
| 11 | CuCl2 | Py (2) | 1,4-Dioxane | 0 | |
| 12 | CuBr2 | Py (2) | 1,4-Dioxane | 0 | |
| 13 | CuOAc | Py (2) | 1,4-Dioxane | <5 | |
| 14 | CuBr | Py (2) | 1,4-Dioxane | 0 | |
| 15 | Cu(OAc)2 | Ag2O | Py (2) | 1,4-Dioxane | 25 |
| 16 | Cu(OAc)2 | TBHP | Py (2) | 1,4-Dioxane | 10 |
| 17 | Cu(OAc)2 | (tBuO)2 | Py (2) | 1,4-Dioxane | 44 |
| 18 c | Cu(OAc)2 | (tBuO)2 | Py (2) | 1,4-Dioxane | 59 |
| 19 c | Cu(OAc)2 | (tBuO)2 | Py (2) | DME | 46 |
| 20 c | Cu(OAc)2 | (tBuO)2 | Py (2) | THF | 40 |
| 21 c | Cu(OAc)2 | (tBuO)2 | Py (2) | Toluene | 15 |
| 22 c | Cu(OAc)2 | (tBuO)2 | Py (2) | DME–1,4-dioxane (7 : 3) | 84 |
| 23 c | Cu(OAc)2 | (tBuO)2 | Py (1) | DME–1,4-dioxane (7 : 3) | 50 |
| 24 c | Cu(OAc)2 | (tBuO)2 | Py (3) | DME–1,4-dioxane (7 : 3) | 96 (92) |
| 25 c d | Cu(OAc)2 | (tBuO)2 | Py (3) | DME–1,4-dioxane (7 : 3) | 63 |
| 26 c | Cu(OAc)2 | (tBuO)2 | — | DME–1,4-dioxane (7 : 3) | 0 |
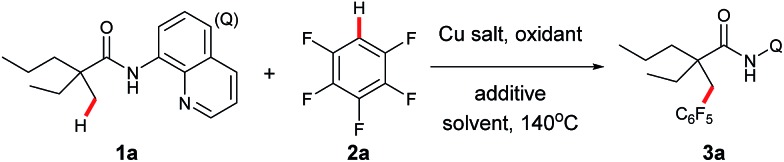
aReaction conditions: 1a (0.3 mmol), 2a (0.6 mmol), Cu salt (0.3 mmol), oxidant (0.75 mmol), additive, 1.0 mL of solvent, 140 °C, 16 h.
bYields and conversions are based on 1a, determined by 1H-NMR using dibromomethane as the internal standard. Isolated yield is in parenthesis.
cUnder N2 atmosphere.
dCu(OAc)2 (0.15 mmol). Q = 8-quinolinyl.
