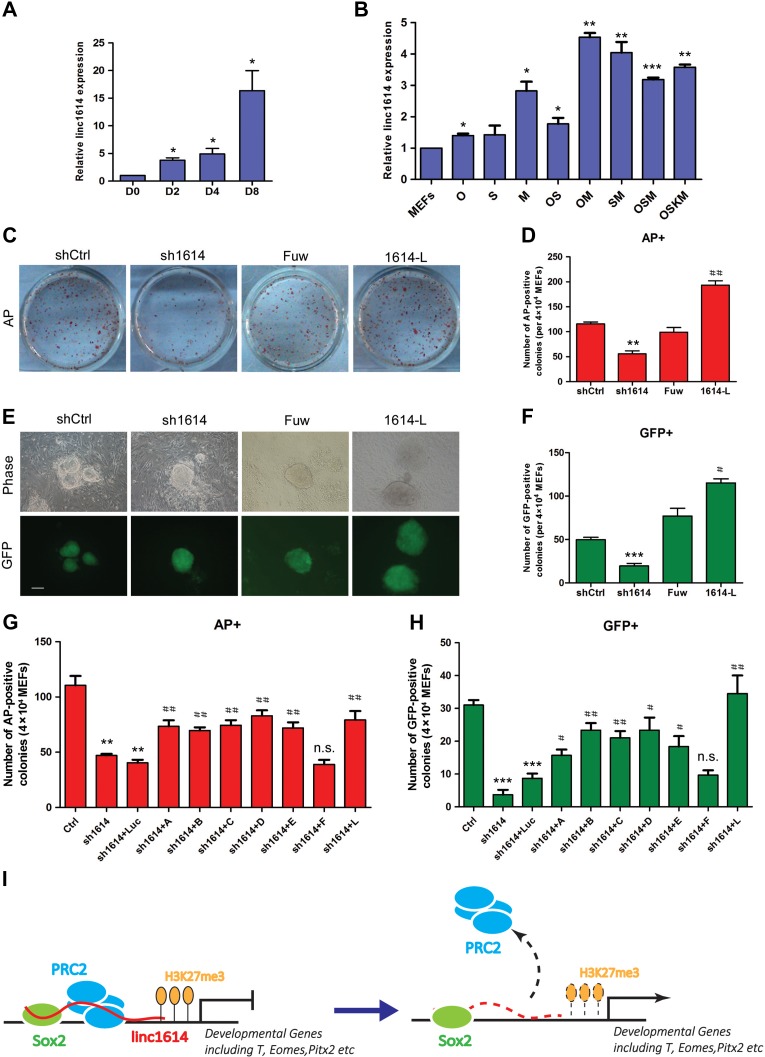
Figure 5.
Linc1614 is required for somatic cell reprogramming. (A) The change of linc1614 expression level was gradually increased during the days (0, 2, 4, and 8) of iPSC induction. *P < 0.05 relative to D0. (B) Analysis for changes of linc1614 expression level upon overexpression of defined factors (O, Oct4; S, Sox2; M, c-Myc) alone or in combination (OS, OM, SM, OSM, and OSKM). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 relative to MEFs. (C and D) AP staining (on reprogramming Day 8) and statistics for AP-positive colonies from OG-MEFs (per 4 × 104 cells) transduced with OSKM in combination with linc1614 knockdown (sh1614) or linc1614 overexpression (1614-L). shCtrl represented scramble shRNA with no specific target. Fuw represented empty vector. (E and F) Representative images and statistics for GFP-positive iPSC colonies on Day 10 of OSKM-induced reprogramming in combination with sh1614 or 1614-L. Scale bar, 100 μm. Data were presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). Student’s t-test was performed for significance (*,#P < 0.05, **,##P < 0.01, and ***,###P < 0.001). * relative to shCtrl and # relative to Fuw. (G and H) The statistics for the AP-positive colonies (G) and GFP-positive colonies (H) showed that introduction of the linc1614 fragments that bound to Sox2 significantly rescued the efficiency of iPSC induction blocked by the knockdown of linc1614. Ctrl represented scramble shRNA. Data were presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). Student’s t-test was performed for significance (*,#P < 0.05, **,##P < 0.01, and ***,###P < 0.001). * relative to Ctrl and # relative to sh1614 + luc. (I) Schematic diagram of the mechanism through which Sox2 cooperates with linc1614 to recruit the PRC2 complex and repress the expression of developmental genes such as T, Eomes, and Pitx2 in pluripotent cells.