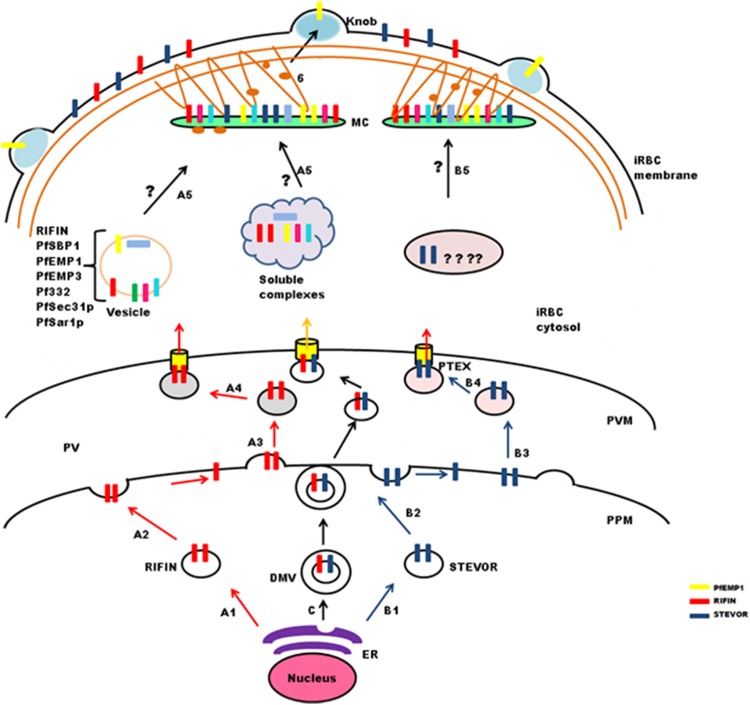
Figure 4. Schematic representation of possible trafficking pathways for STEVOR and RIFIN proteins.
After synthesis and processing in the parasite ER budding vesicles are generated (StepA1 and B1), that fuse with the parasite plasma membrane (PPM) (Step A2 and B2), new vesicles are released (StepA3 and B3), that deliver proteins to the PTEX for export across the parasitophorous vacuole membrane (PVM) (StepA4 and B4). Trafficking may occur in the form of double membrane vesicles (DMVs) (C). RIFIN proteins are transported to Maurer’s cleft either in the form of vesicles or soluble protein complexes (StepA5), while the exact pathway for STEVORs remains elusive (StepB5), Proteins transiently localize to MCs before they are transported to the iRBC membrane possibly by vesicles treadmilling on actin filaments (Step6). Brown threads represent actin filaments.