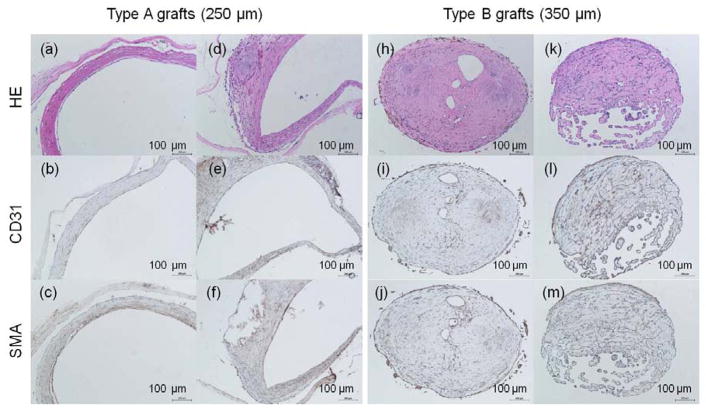
Figure 8.
H&E images of harvested poly(1-LEU-10) grafts at 12 months after implantation (a, d, h, k); Endothelial layer of graft lumen stained by CD31 markers (b, e, i, l); Smooth muscle cells stained by immunohistochemical smooth muscle actin (aSMA) (c, f, j, m). Extensive tissue remodeling in type A grafts leads to the development of well-circumscribed neovessels with an endothelial inner lining, a neointima containing smooth muscle cells. However, this well-organized endothelium and smooth muscle layers were absent in type B grafts.