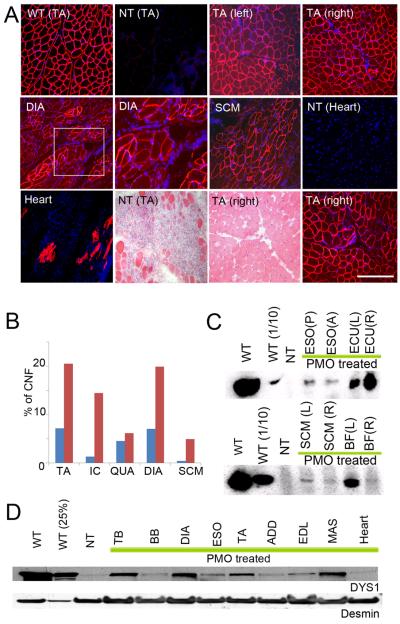
Figure 4. Wide-spread dystrophin expression and improved histology by intravenous systemic delivery of cocktail morpholinos in CXMD dogs.
(A) Dystrophin (DYS1) staining and histology in bilateral tibialis anterior muscles (TA), diaphragm (DIA), sternocleidomastoid (SCM) and heart at 2 weeks after final injection after 5 × weekly iv injection of 120 mg/kg of cocktail morpholinos containing Ex6A, Ex6B, and Ex8A (2001MA). Comparisons were made with TA from normal control (wild-type; WT) and from non-treated CXMD littermate (NT) tibialis anterior (TA) and heart. Intravenous morpholino treatment resulted in extensive though variable dystrophin production in multiple muscles, but with only limited evidence of rescue in heart (isolated cardiocytes). Paired dystrophin immunostaining and histology from treated dog (TA, lower panels) showed improved histopathology relative to untreated littermate (NT TA) histology. Bars; 200 μm, except for higher magnification picture of DIA and hearts (100 μm).
(B) Quantitation of centrally nucleated fibers (CNFs) in TA, intercostal (IC), Quadriceps (QUA), diaphragm (DIA), and sternocleidomastoid (SCM) in treated dog (blue bars; 2001MA) and untreated dog (red bars; 2008MA).
(C) Western blotting analysis for detection of dystrophin at 2 weeks after final injection after 5 × weekly iv injection of 120 mg/kg of cocktail morpholinos containing Ex6A, Ex6B, and Ex8A (2001MA). Dystrophin rescue is variable with high expression in right extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU(R)) and left biceps femoris (BF(L)), and less in posterior or anterior esophagus (ESO(P), ESO(A)), and sternocleidomastoid (SCM).
(D) Immunoblot analysis of dystrophin in intravenous morpholino treated dog (2703MA; 7× weekly dosing) and controls (normal control [WT], non-treated [NT]). Desmin immunoblot is shown as a loading control. Dystrophin shows high levels (>25% control levels) in triceps brachii (TB), diaphragm (DIA) and masseter (MAS).
ESO Esophagus (posterior or anterior); ECU, Extensor carpi ulnaris; SCM, Sternocleidomastoid; BF, Biceps Femoris; TB, Triceps Brachii; BB, Biceps Brachii; DIA, Diaphragm; ADD, Adductor; EDL, Extensor digitorum longus; MAS, Masseter.