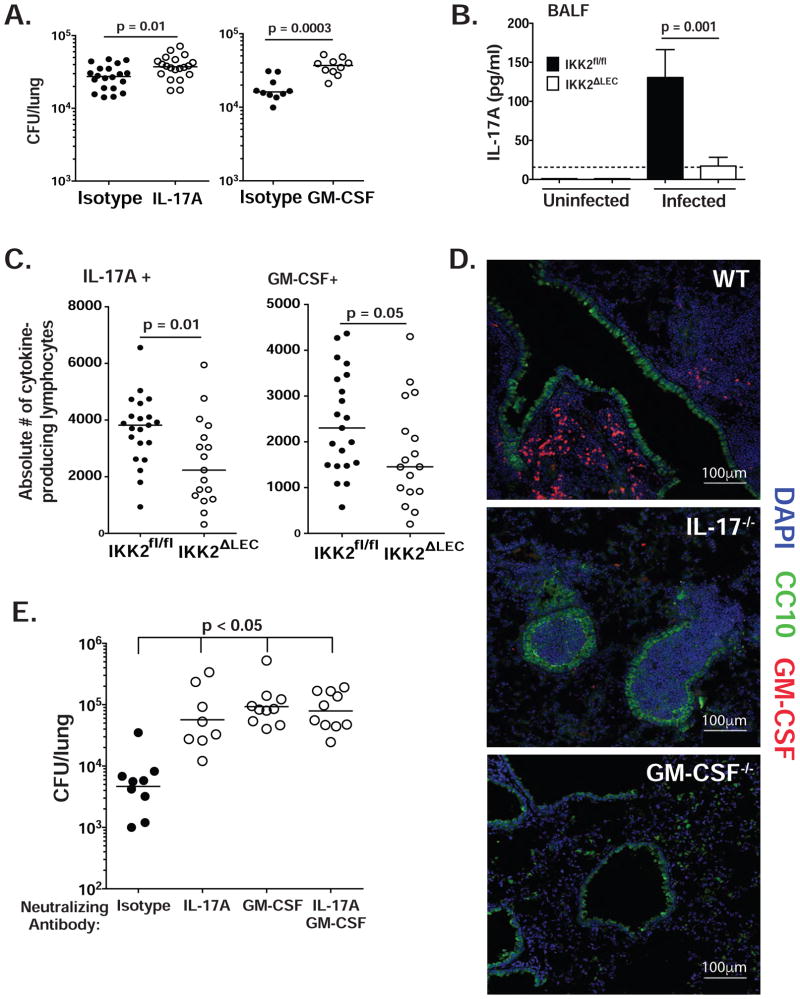
Figure 2. LEC-mediated antifungal immunity is IL-17A- and GM-CSF-dependent (see also Fig. S2).
(A) WT mice were infected i.t. with yeast. IL-17A and GM-CSF were neutralized as noted in Methods. At 48 h.p.i., lung CFU was enumerated. Each panel represents a separate experiment (2 pooled experiments depicted in left panel); each symbol denotes one mouse. Mann-Whitney test (48 h.p.i.). (B) IKK2fl/fl and IKK2ΔLEC mice were infected i.t. with yeast and IL-17A content was analyzed by ELISA in BALF at 48 h.p.i. A representative of 4 experiments is depicted. Mann-Whitney test. (C) IKK2fl/fl and IKK2ΔLEC mice were infected i.t. with yeast. At 48 h.p.i., lung cell suspensions were analyzed by flow cytometry for intracellular IL-17A and GM-CSF in lymphocytes (CD90.2+ CD44hi). Two pooled experiments depicted. Mann-Whitney test. (D) WT, IL-17A−/− and GM-CSF−/− were infected with 5×105 yeasts; at 48 h.p.i., lungs were analyzed by confocal imaging. Club cells depicted in green (CC10), nuclei in blue (DAPI) and GM-CSF in red. (E) Procedure was done as in A with one further injection of antibody at 48 h.p.i. At 96 h.p.i., lung CFU were quantified. Data representative of 3 experiments. Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn’s multiple comparison.