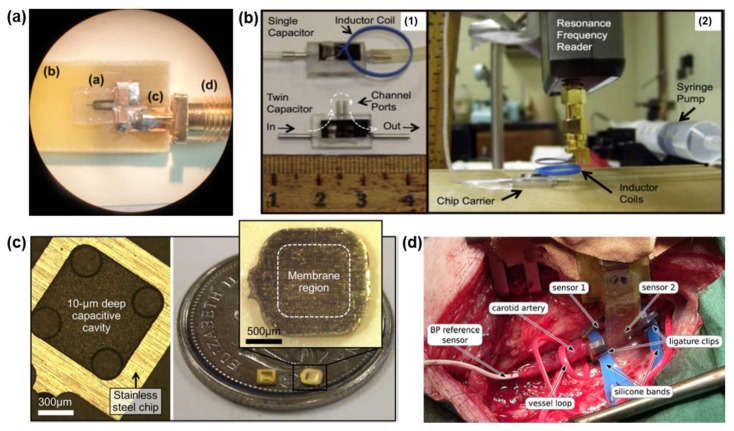
Figure 1.
(a) Assembled blood pressure sensing device; (a) pressure sensor on, (b) FR-4 test board with, (c) transmission line, and (d) SubMiniature version A (SMA) connector. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [18], Copyright (2013), Springer Nature; (b) Flow sensors for cerebrospinal fluid sensing: (1) Test sensors with a single capacitor with inductor coil attached (top) and a twin-capacitor sensor without inductor coils (bottom); (2) Flow control unit (syringe pump) and spectrometer (resonance frequency reader) with a test sensor on a chip carrier. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [24], Copyright (2015), Elsevier; (c) Fabricated intravascular pressure sensors: (left) with a stainless-steel chip before membrane bonding and completed sensors; (right) a close-up of the diaphragm. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [27], Copyright (2014), Spring Nature; (d) Photograph of the optical blood pressure sensor units mounted onto the carotid artery of a domestic pig. The photo shows the operation site before measurement. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [35], Copyright (2012), Springer Nature.