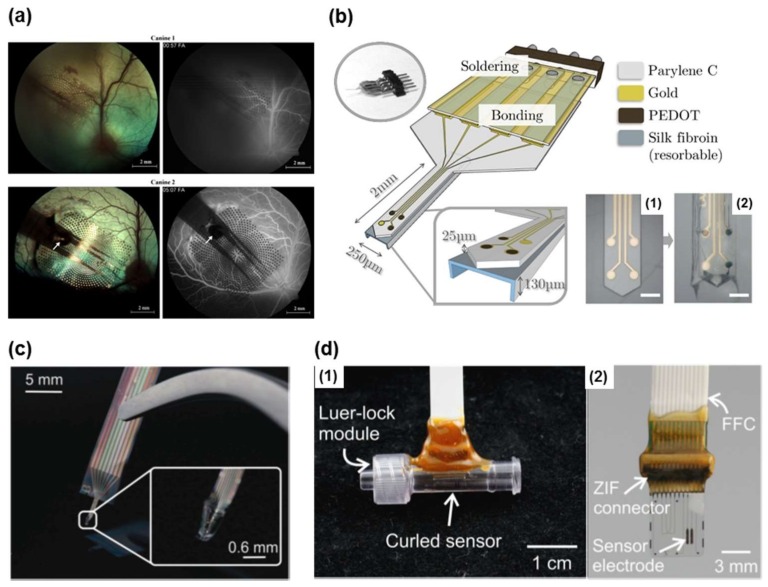
Figure 4.
(a) Fundus photographs (left) showing parylene multi-electrode arrays (MEAs) tacked to the right retina of both animals, and fluorescein angiographies (FAs) (right) showing normal vessel perfusion under the arrays. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [62], Copyright (2008), Elsevier; (b) Schematic representation of a parylene C-based neural probe with three poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT)-nanostructured electrodes (40 µm in diameter), and one gold electrode as control. Two photographs show the probe tip 1 before and 2 after PEDOT nano-structuration and silk integration (scale bar 150 µm). Reprinted with permission from Ref. [91], Copyright (2017), Elsevier; (c) Fabricated flexible parylene sheath neural probe with integrated parylene cable. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [61], Copyright (2012), Royal Society of Chemistry; (d) 1 Packaged patency sensors in inline modules for benchtop testing; 2 Electrically packaged parylene device with final electrode design using a ZIF connector and integrated flat flexible cable (FFC). Reprinted with permission from Ref. [59], Copyright (2016), Springer Nature.