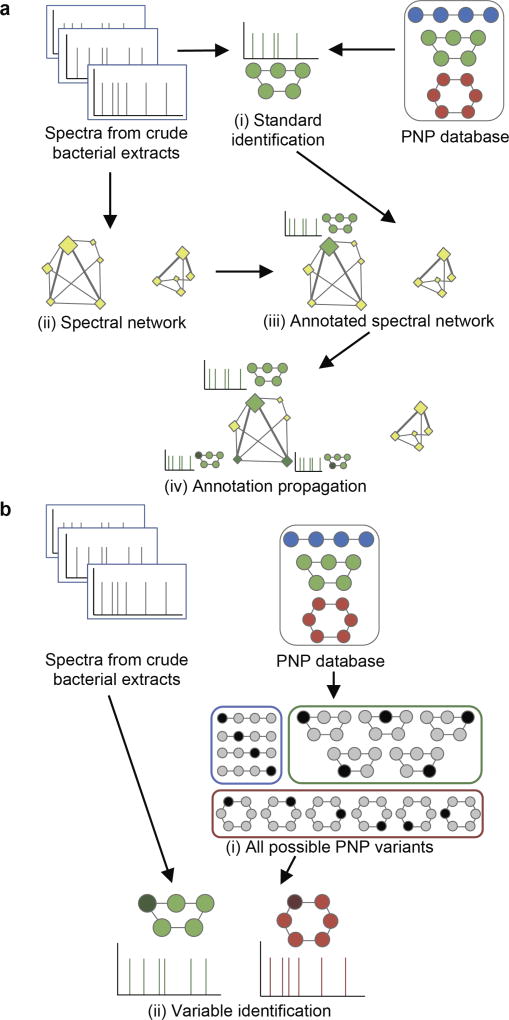
Figure 1. Network-based and network-independent strategies for variable PNP identification.
Variant PNPs are colored by the same color as their known compounds in the database; modified/mutated amino acids are highlighted by darker color. (a) Network-based PNP identification starts from the standard identification of spectra (i) and construction of a spectral network (ii). Next, the network is annotated (iii) using the identified PNPs via the spectral network propagation approach. In this example, the network component on the left has a single unmodified parent colored green as the related PNP, while the component on the right is an orphan. Annotation propagation (iv) through the network results in two variable PNP identifications represented by additional green nodes. (b) Network-independent PNP identification relies on an efficient enumeration of all PNP variants (i) and further matching of spectra against these variants using the standard identification strategy (ii).