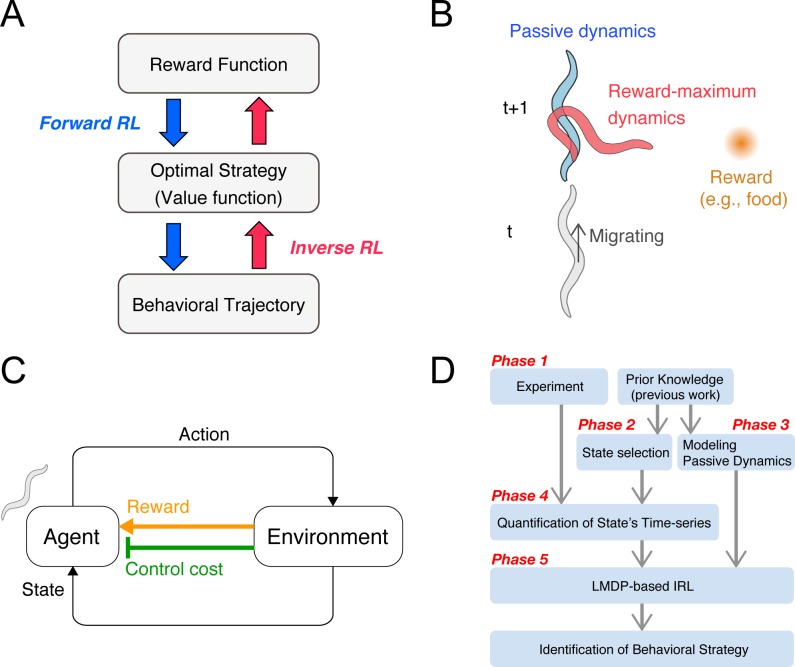
Fig 1. Concept and procedure of the inverse reinforcement learning (IRL)-based approach.
(A) Reinforcement learning represents a forward problem, in which a behavioral strategy is optimized to maximize the cumulative reward given as a series of states and rewards. IRL represents an inverse problem, in which a behavioral strategy, or its underlying value and reward functions, is estimated in order to reproduce an observed series of behaviors. The behavioral strategy is evaluated by the profiles of the identified functions. (B) Examples of passive and controlled dynamics. An animal migrates upwards, while the food (reward) is placed to its right. In this situation, if the animal continues to migrate upwards, the distance to the food increases. If the animal exercises harder body control, that is, changes its migrating direction towards the food, the distance to the food decreases. The animal should therefore make decisions based on balancing these two dynamics. (C) The agent-environment interaction. The agent autonomously acts in the environment, observes the resultant state-transition through its sensory system, and receives not only a state reward but also a body control cost. The behavioral strategy is optimized to maximize the accumulation of the net reward, which is given as the state reward minus the body control cost. (D) IRL framework for the identification of animal behavioral strategies. If a certain behavioral strategy is under investigation, a behavioral experiment is initially performed (phase 1), which can either involve a free-movement task or a conditional task. Subsequently, the states and passive dynamics, based on which the animal develops its strategy, are selected and modelled (phase 2 and 3). For these phases, prior knowledge on the type of sensory information an animal processes is useful for appropriately selecting the states and passive dynamics. Phases 4 and 5 involve the quantification of the time-series of the selected states and the implementation of the linearly-solvable Markov decision process-based IRL, respectively, in order to estimate the value function. The behavioral strategy can be then identified.