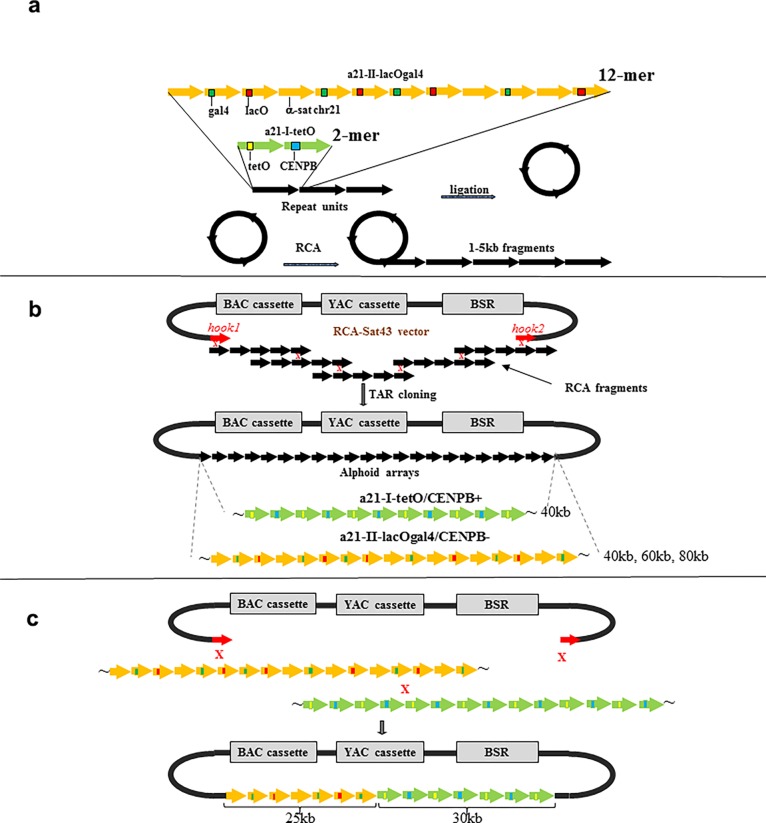
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of construction of synthetic tandem arrays. (a) Step one includes amplification of either a 2,078 bp 21-II-lacOgal4 12-mer or a 343 bp 21-I-tetO dimer by rolling circle amplification (RCA) reaction up to 1–3 kb fragments. (b) Step two includes construction of long alphoid arrays by transformation-associated recombination (TAR) cloning in yeast. The RCA-amplified fragments are cotransformed into yeast cells along with the MluI-linearized RCA-Sat43 vector (the MluI restriction site is located between the hooks). This vector contains a BAC cassette (a BAC replicon and a Clm marker), a YAC cassette (a selectable marker HIS3, a centromere sequence CEN6 from yeast chromosome VI, and yeast origin of replication ARSH4), and a mammalian marker Bsr (the blasticidin gene) that allows the vector to propagate in yeast, bacterial, and mammalian cells and alphoid-specific hooks of 40 bp each (Ebersole et al. 2005). Recombination of the RCA-amplified fragments accompanied by their recombination with the hooks results in the rescue of long arrays as circular YAC/BACs, and 40 kb α21-I-tetO and 40 kb α21-II-lacOgal4 arrays were chosen for further experiments. (c) Construction of the hybrid tetO-CENPB+-lacOgal4-CENPB– array. Recombination between the arrays accompanied by their recombination with the vector hooks leads to formation of the hybrid arrays. Ultimately, a molecule containing a 20 kb lacOgal4 array and 25 kb tetO array was chosen for HAC formation.