Figure 3.
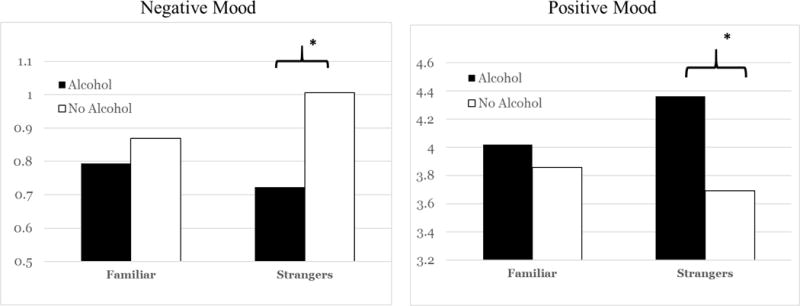
Results revealed a significant interaction between social familiarity and alcohol consumption in predicting positive mood and negative mood in everyday drinking settings. The above graphs reflect the interaction between alcohol and the familiarity variable Average Time Spent, centered at 1SD above and below the mean (-SD was equivalent to “0 hours,” labeled above as ―strangers‖).
