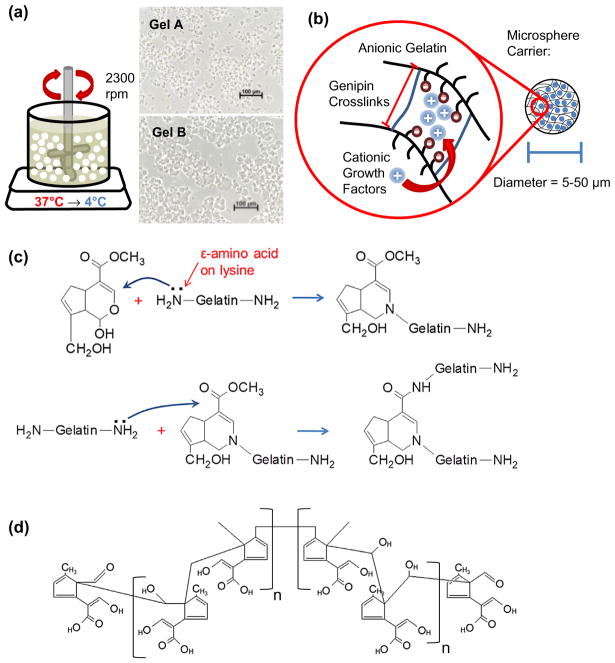
Figure 1.
Gelatin microsphere emulsification, crosslinking, and growth factor loading. (a) Schematic of the gel emulsification technique used to produce gelatin microspheres. Insets show microspheres made from gelatin Type A and gelatin Type B prior to crosslinking. (b) Schematic of genipin crosslinking of the gelatin matrix and the resulting mesh size and charge affinity. Cationic growth factors can bind to the anionic gelatin via electrostatic interactions. (c) Crosslink mechanism described by Butler, Ng, and Pudney (2003) showing reactivity of genipin with lysine primary amines found in gelatin. (d) Structure of genipin polymer proposed by Mi, Shyu, and Peng (2005) after undergoing ring-opening polymerization at basic pH.