Figure 6. RGS14 is expressed in CA1 and CA2 pyramidal cell bodies and neuropil in the monkey hippocampus.
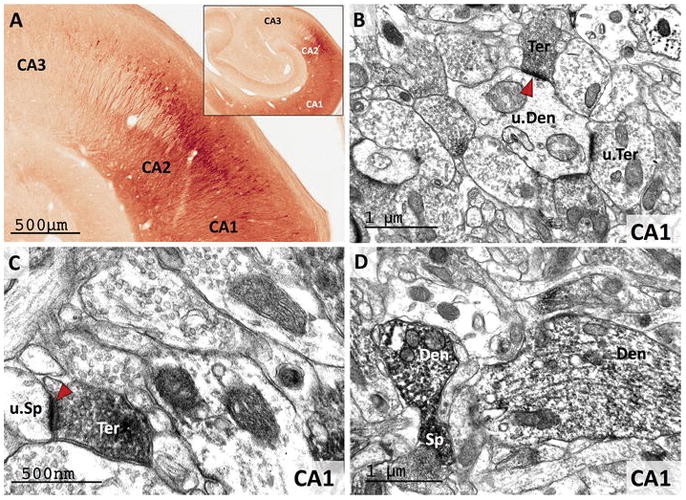
(A) Light microscopy reveals dense RGS14 labeling of pyramidal cell bodies in CA2. By contrast, there is virtually no labeling in CA3. CA1 displays a lighter RGS14 labeling than CA2, which is preferentially localized in the neuropil. (B and C) Electron micrographs of RGS14-positive terminals (Ter) forming asymmetric axo-dendritic (B) or axo-spinous (C) synapses in CA1. In each micrograph, RGS14-immunoreactive axon terminals (Ter), spines (Sp) and dendrites (Den) are indicated, while u.Ter, u.Sp, and u.Den mark unlabeled corresponding elements. The red arrowheads point at asymmetric synapses that involve RGS14-containing terminals, which likely originate from CA2-CA1 axonal projections. (D) Post-synaptic RGS14 labeling in CA1 dendrites and spines.
