Fig. 2. Summary diagram of adverse maternal and fetal effects associated with IVF.
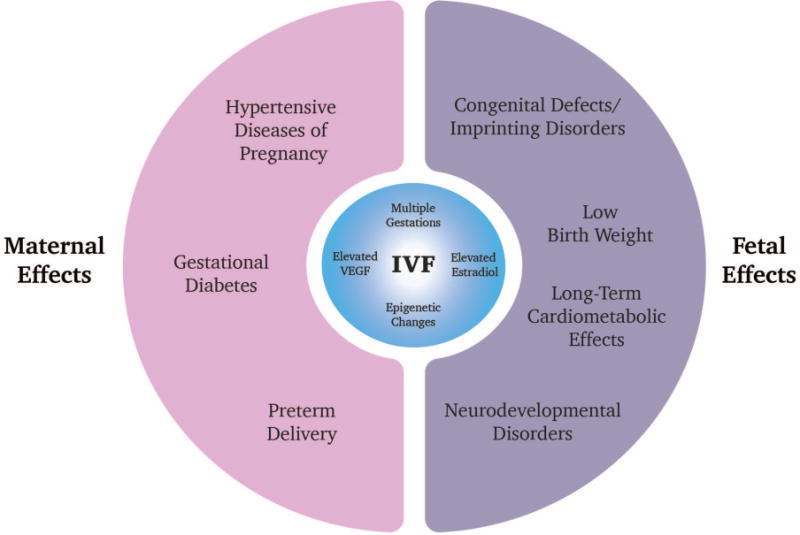
Adverse maternal outcomes associated with IVF include hypertensive diseases of pregnancy, gestational diabetes, and preterm delivery. Fetal effects include low birth weight, congenital defects/imprinting disorders, as well as potentially neurodevelopmental disorders and long-term cardiometabolic effects. The risk of multiple gestations in IVF pregnancies is the main driver for these outcomes, but other mechanisms are actively being investigated. Features of IVF including hormonal stimulation which leads to increased estradiol and VEGF levels may contribute. Epigenetic alterations in imprinted genes after hormonal stimulation and embryo culture may also be a driver for some of these adverse outcomes.
