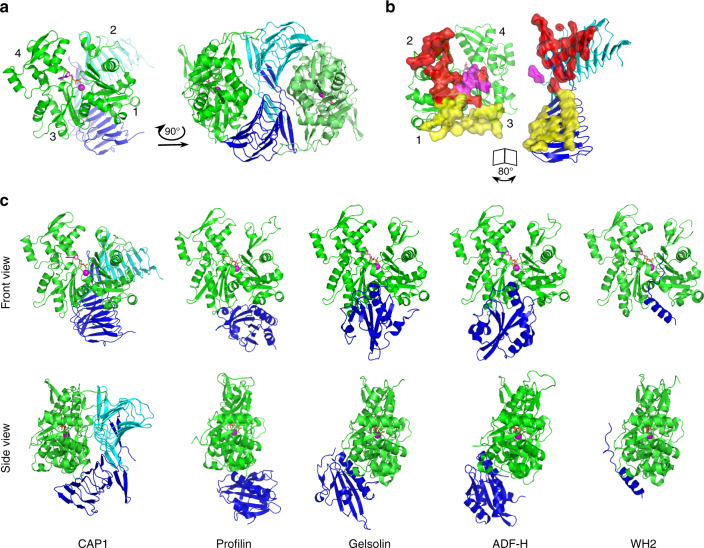
Fig. 1.
Crystal structure of the CARP domain from mouse CAP1 in complex with ADP-actin. a CARP domain forms a homodimer (the subunits are in blue and cyan) that binds two actin molecules (in green) through their subdomains 1, 2, and 3. b The CARP domain dimer covers a large surface (1944 Å2) on each actin monomers. The two subunits of the CARP domain dimer employ two different interfaces (primary interface in yellow; secondary interface in red; and C-terminal tail of CARP from the secondary interface in magenta) for association with each actin monomer. c Structural comparison of actin monomer-binding mechanisms of CARP domain of CAP1 (6fm2), profilin (2btf)44, gelsolin segment-1 (1eqy)45, ADF-H domain of twinfilin (3daw)46, and WH2 domain of ciboulot (1sqk)47. Front and side views of the complexes are shown. PDB entries are indicated in brackets