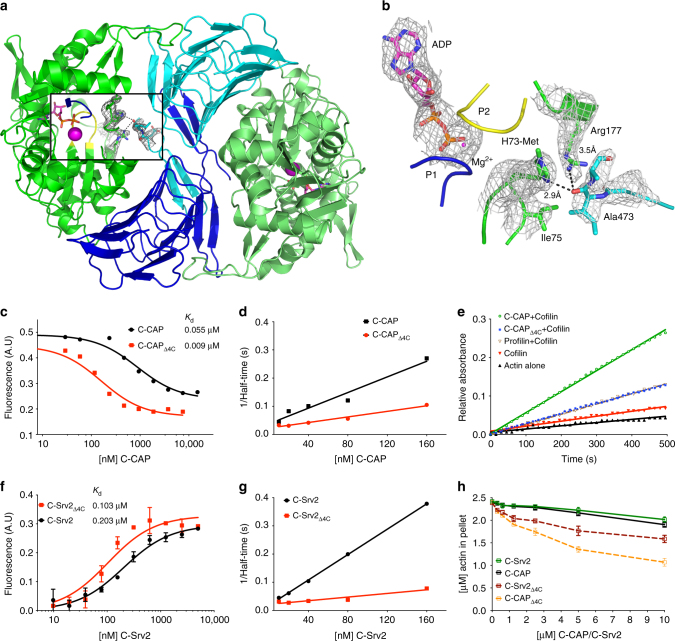
Fig. 4.
The C-terminal tail of CAP is critical for nucleotide exchange. a C-terminal tail of CAP1 in the crystal structure displayed in 2F0–FC (σ = 1.0) electron density map. b Tail is positioned next to the nucleotide sensing region, loops P1 and P2 of actin that coordinate the nucleotide (σ = 1.0 in 2F0–FC electron density map). c The affinity of C-CAP and C-CAPΔ4C for ADP-G-actin was determined by a fluorometric competition assay with NBD-labeled actin (0.18 μM) and the C-terminal ADF-H domain of mouse twinfilin (0.44 μM) (see Supplementary Fig. 4a). d A representative example of rate of ADP-G-actin (0.5 µM) nucleotide exchange in the presence of different concentrations of wild-type C-CAP and C-CAPΔ4C. e A representative example of actin filament turnover as followed by Pi-release. F-actin (20 µM) was mixed with the indicated proteins (each 5 µM). f The affinity of C-Srv2 and C-Srv2Δ4C for ADP-G-actin (0.18 µM) was determined by fluorometric NBD assay. n = 3, error bars represent SD. g A representative example of rate of ADP-G-actin (0.5 µM) nucleotide exchange in the presence of C-Srv2 and C-Srv2Δ4C. h Monomer sequestering assay for C-CAP and C-Srv2 with different C-CAP/C-Srv2 concentrations using 2.5 µM actin. n = 3, error bars represent SD