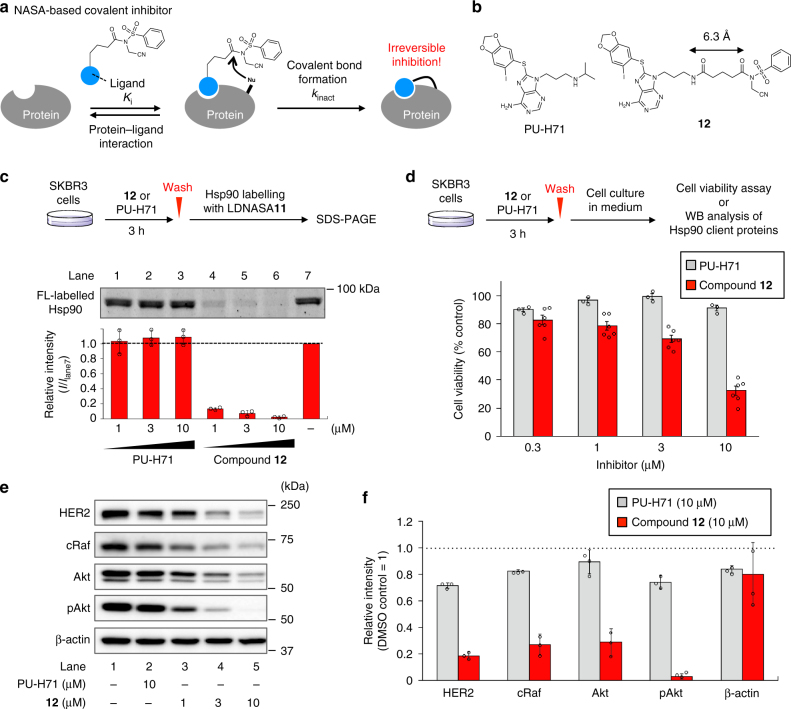
Fig. 6.
Irreversible inhibition of intracellular Hsp90. a Schematic illustration of reaction mechanism of NASA-based covalent inhibitor. b Molecular structures of PU-H71 (non-covalent inhibitor) and NASA-based covalent inhibitor 12. c In-gel fluorescence analysis of fluorescein labelling of Hsp90 with 11 in SKBR3 cells after inhibitor washout. After cells were incubated with various concentrations of PU-H71 or 12 for 3 h, the cells were washed with medium and further incubated with 11 for 3 h. The cells were washed, lysed and analysed by in-gel fluorescence imaging. Error bars represent s.d., n = 3. d Viability of the cells 69 h after PU-H71 or 12 washout. Data represent mean values ± standard error of the mean (s.e.m.) for three (PU-H71) or six (compound 12) independent experiments. e Western blotting analysis of the destabilization of client proteins induced by inhibiting Hsp90 chaperone activity, and f the normalised band intensities. Cells were treated with PU-H71 or 12 for 3 h, followed by washing with media and further incubation for 21 h. The protein band intensity was normalised to DMSO control (lane 1). β-actin is a control as a non-Hsp90 client protein. Error bars represent s.d., n = 3