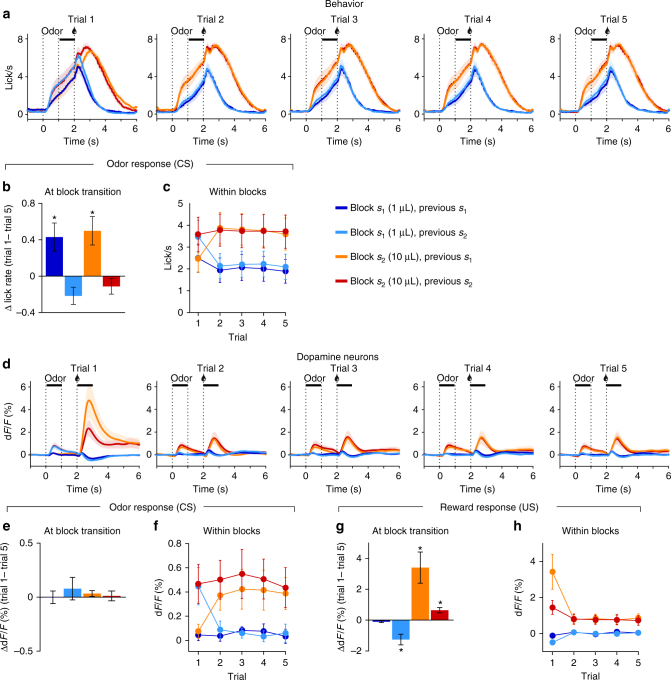
Fig. 2.
Behavior and dopamine neuron activity on training blocks s1 and s2. a Licking across the five trials within a block. Anticipatory licking quantification period during odor to reward delay is indicated by the horizontal black line. b Anticipatory licking at block transition increases when transitioning from the small to the big block. c Anticipatory licking across trials within blocks. Anticipatory licking on trial 1 is similar across all block types then stabilizes at either low or high rates for the following four trials. d Dopamine neuron activity across the five trials within a block. Horizontal black line indicates quantification period for odor (CS) and reward (US) responses. e Dopamine neurons odor response across block transitions is stable. f Dopamine neurons odor response across trials. Dopamine activity adapts to the current block value within one trial. g Dopamine neurons reward response shows an effect of the current reward and previous block on trial 1. h Dopamine neurons reward response across trials. Dopamine activity reaches stable levels as from trial 2. Data represents mean ± s.e.m. *p < 0.05 for t-test comparing average value to 0. n = 11 mice