Fig. 3.
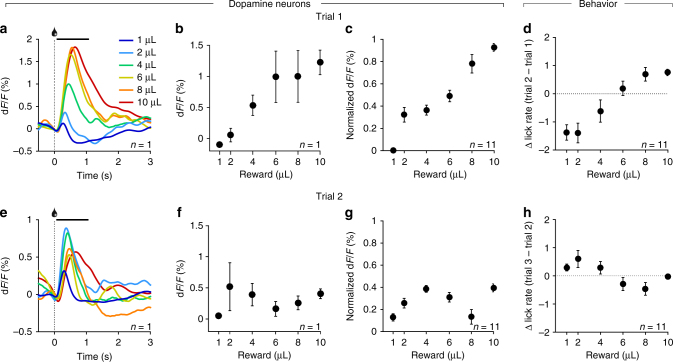
Dopaminergic and behavioral signature of belief states. a–c Dopamine neurons activity on trial 1. Dopamine neurons show a monotonically increasing response to increasing rewards (a, individual example), quantified as the mean response after reward presentation (0–1 s, indicated by a solid black line in a) in the individual example (b) and across mice (c). d Change in anticipatory licking from trial 1 to trial 2. Mice increase their anticipatory licking after trial 1 proportionally to the increasing rewards. e–g Dopamine neurons activity on trial 2. Dopamine neurons show a non-monotonic response pattern to increasing rewards (e, f, individual example), quantified across all mice (g). h Change in anticipatory licking from trial 2 to trial 3. Whereas mice do not additionally adapt their licking for the known trained volumes (1 and 10 μL) after trial 2, they increase anticipatory licking for small intermediate rewards and decrease it for larger intermediate rewards in a pattern, which follows our prediction of belief state influence on RPE. n = 11, data represent mean ± s.e.m.