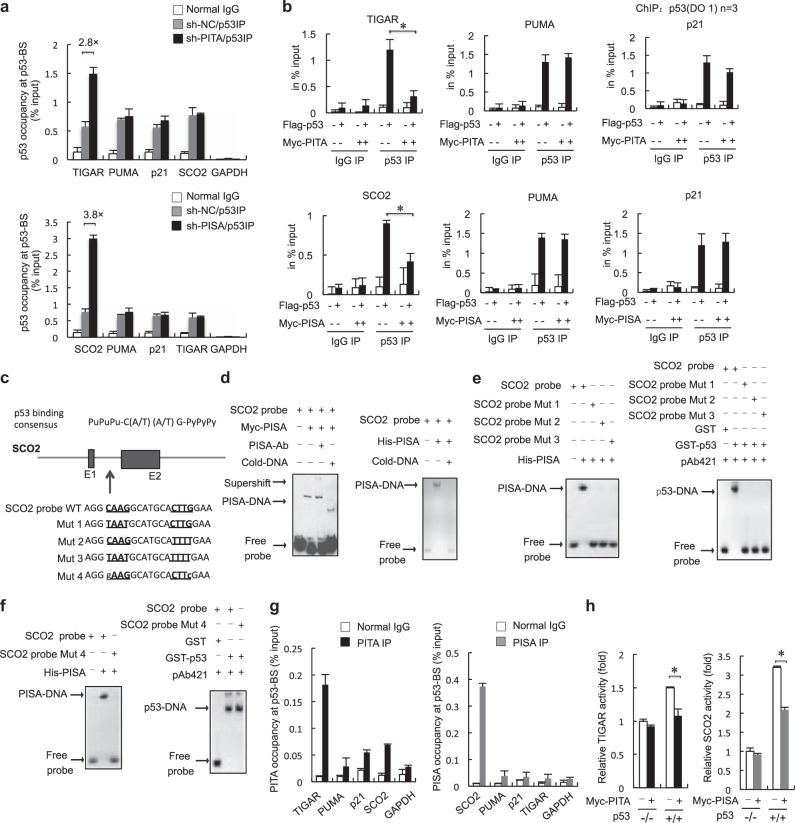
Fig. 2.
PITA and PISA preferentially inhibit the binding of p53 to the target genes TIGAR and SCO2, respectively. a ChIP assays in PITA-knocking down and PISA-knocking down or control p53+/+ HCT116 cells. IP immunoprecipitation. b Multiple ChIP analysis on the consensus binding sequences of p53 targets. HCT116p53−/− cells were transfected with a mock vector, PITA, p53, or cotransfected with p53 and PITA as indicated (top), HCT116p53−/− cells were transfected with a mock vector, PISA, p53, or cotransfected with p53 and PISA as indicated (bottom). After 24 h, ChIP was carried out using a control mouse IgG or an anti-p53 antibody, and RT-PCR was performed for the indicated promoters. c The p53-binding sequence in the promoter or intron of SCO2 is shown. For intron 1, the PISA-binding core sequence is underlined. PISA binds to the PISA/p53-BS of SCO2 in vitro. d Supershift EMSA using nuclear extracts derived from p53−/− HCT116 cells harboring Myc-PISA. The PISA antibody and an unlabeled competitor probe were added as indicated. EMSA was performed with 100 ng of His-PISA and biotin-labeled PISA/p53-BS oligonucleotides. e, f EMSA of the p53 protein with PISA/p53-BS and mutants. The mutant PISA/p53-BS probes (for sequences, see c) were used in the EMSA with PISA protein. The mutant probes were used in the EMSA with the p53 protein and p53 antibody. EMSA was performed with 100 ng His-PISA and biotin-labeled mutant PISA/p53-BS. g ChIP assays in p53+/+ HCT116 cells. The promoter or intron of the indicated p53 target genes were amplified from immunoprecipitates of anti-PITA, anti-PISA, or IgG control. GAPDH was used as an internal control. h p53−/− and p53+/+ HCT116 cells were co-transfected with TIGAR/p53-BS-Luc and PITA or SCO2/p53-BS-Luc and PISA, and the luciferase activity was measured. Error bars represent mean ± SD for three independent experiments. (a, b, g, h; mean and s.e.m., n = 3. *p < 0.05: two-tailed unpaired t-test). Unprocessed original scans of blots are shown in Supplementary information, Figure S9