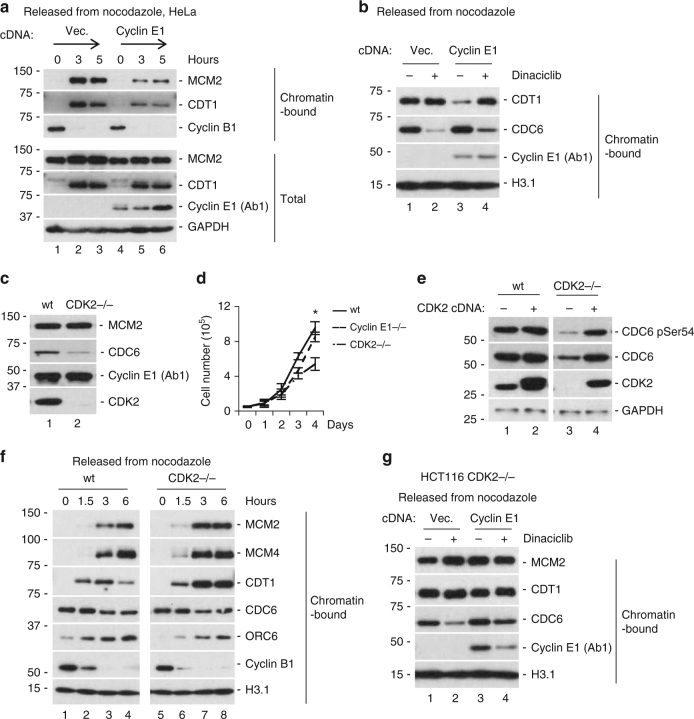
Fig. 6.
Uncontrolled CDK2 activity in G1 inhibits pre-RC assembly. a Ectopic expression of cyclin E1 inhibited pre-RC formation in various cell lines. HeLa cells were transfected with vector control (vec.) or cDNA encoding cyclin E1 (Cyclin E1). Cells were synchronized at M phase and released using the same protocol in previous figures. Similar results were obtained in HEK293 (Fig. 5m) and HCT116 cells (b). b CDK2 inhibitor treatment (dinaciclib, 500 nM) eliminated the negative effect of cyclin E1 on pre-RC assembly. HCT116 cells were transduced with vector control (vec.) or cDNA encoding cyclin E1 (Cyclin E1). Cells were synchronized at M phase and released into fresh medium with or without small-molecule CDK2 inhibitor. c CDC6 protein level was reduced in CDK2 knockout HCT116 cell lines. Similar results were obtained in several independent cell lines. Knockout cell lines were generated by CRISPR/Cas9 technology. d Growth curve comparison of wild-type (wt), cyclin E1 knockout (Cyclin E1−/−) and CDK2 knockout (CDK2−/−) HCT116 cell lines. Data are means ± SEM (n = 3) (*p < 0.05; Student’s t-test; CDK2−/− compared to wt). e CDK2 overexpression did not increase CDC6 protein level. Ectopically expressed CDK2 was functional because it restored CDC6 protein level in CDK2 knockout HCT116 cells. f The kinetics of pre-RC assembly was comparable in wild-type and CDK2 knockout HCT116 cells. g CDK2 knockout eliminated the negative effect of cyclin E1 on pre-RC assembly, consistent with CDK2 inhibitor treatment (b). All experiments were repeated at least three times and representative results are shown