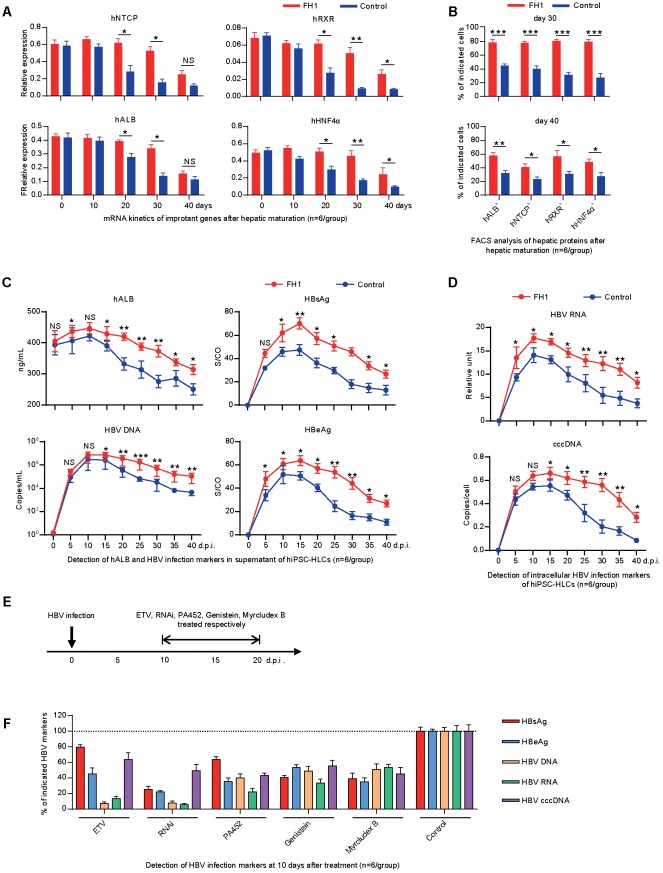
FIGURE 2.
Differentiated hepatic cells were long maintained to support a long-term genotype C HBV infection. (A) Fold changes of the mRNA levels of the human hepatic specific genes in hiPSC-HLCs treated with FH1 as compared to that untreated after being normalized to GAPDH (n = 6). The primers were as shown in Supplementary Table 2. (B) FACS analysis for the positive ratio of the hepatic specific genes in hiPSC-HLCs treated with FH1 as compared to that untreated (n = 6). (C) Protein levels of hALB, HBV DNA, HBsAg, and HBeAg in the supernatant, and (D) intracellular HBV RNA and cccDNA of HBV-infected hiPSC-HLCs at different time points (MOI = 200, n = 6). (E) Schematic design of the in vitro ETV, RNAi, PA452, genistein, and Myrcludex B treatments from days 10 to 20 after HBV infection. (F) Detection of relative HBV infection marker suppression of the indicated antivirals at 10 days after treatment (n = 6). S/CO, signal-to-cutoff. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001.