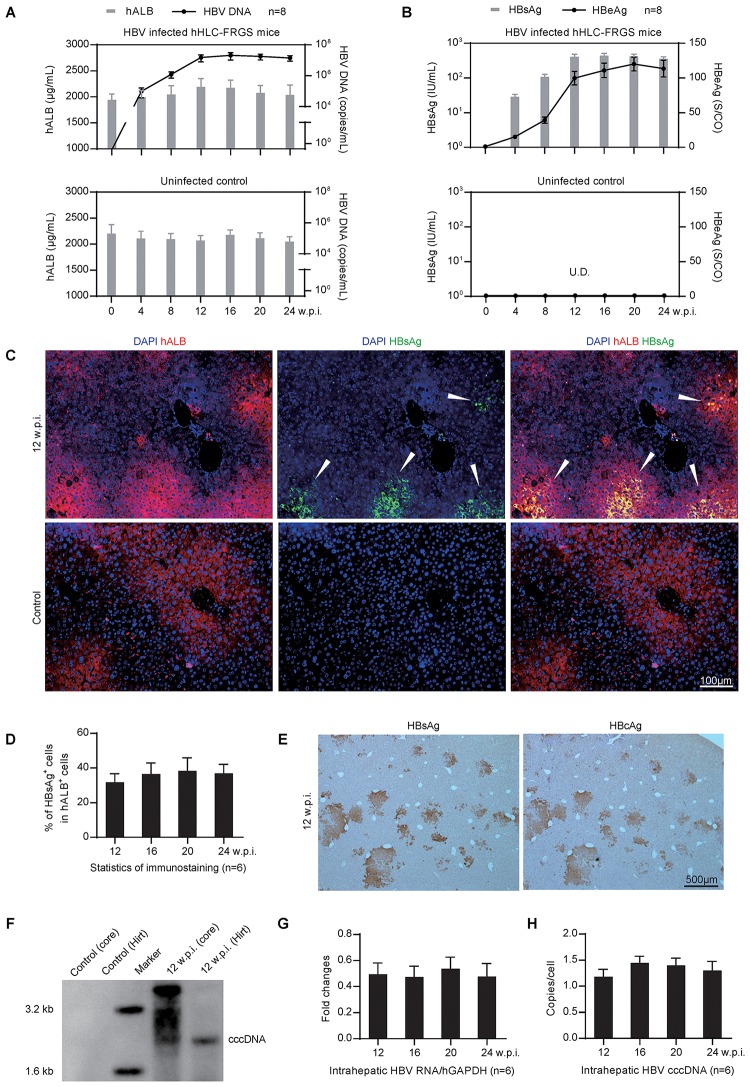
FIGURE 4.
Genotype C HBV infection in hHLC-FRGS mice. (A) Serum hALB and HBV DNA from the HBV infected (upper) or the uninfected (lower) hHLC-FRGS. (B) HBsAg and HBeAg levels from the HBV infected (upper) or the uninfected (lower) hHLC-FRGS by ELISA and qRT-PCR from 0 to 24 w.p.i. (n = 8). (C) ICC for hALB (red) and HBsAg (green) expression in frozen sections of liver tissues collected from uninfected control (lower) and HBV-infected (upper) hHLC-FRGS mice at 12 w.p.i. (bar = 100 μm), and (D) statistics for the different liver lobes collected by partial hepatectomy at the indicated time points (n = 6). (E) IHC staining for HBsAg (left) and HBcAg (right) expression in serial sections of liver tissues collected from HBV-infected hHLC-FRGS mice at 12 w.p.i. (bar = 500 μm). (F) Southern blot analysis of hALB positive cells collected from perfused liver cells of uninfected control and HBV-infected hHLC-FRGS mice at 12 w.p.i., HBV total DNA (core DNA) and cccDNA (by Hirt method) were isolated for detection with 3 × 106 cells for each lane. (G,H) Quantitative analysis of the HBV RNA and cccDNA levels in hALB positive cells collected from HBV-infected hHLC-FRGS mice from 12 to 24 w.p.i. (n = 6). The primers were as shown in Supplementary Table 2.