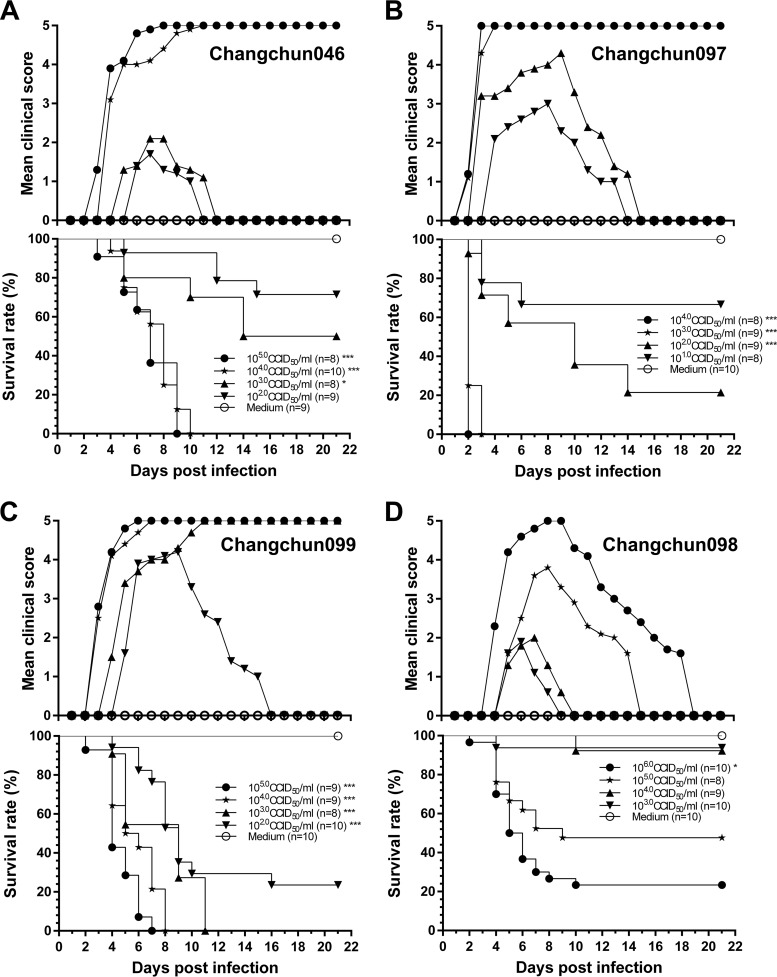
FIG 2.
CV-A6-Changchun viruses cause clinical symptoms and mortality in a dose-dependent manner. One-day-old ICR mice (n = 8 to 10 per litter) were intracerebrally inoculated with 10-fold serially diluted dosages of viruses (10 μl/mouse). Control animals were mock infected with MEM instead of virus (10 μl/mouse). Clinical symptoms and mortality were monitored daily for 21 days postinfection. Neonatal mice were challenged with 102.0 to 105.0 CCID50/ml of Changchun046 virus (A), 101.0 to 104.0 CCID50/ml of Changchun097 virus (B), 102.0 to 105.0 CCID50/ml of Changchun099 virus (C), or 103.0 to 106.0 CCID50/ml of Changchun098 virus (D). The log rank test was used to compare the survival rates of newborn mice between the groups and the control group at 21 days postinfection. ***, P < 0.001; *, P < 0.05. One representative of three independent tests is shown.