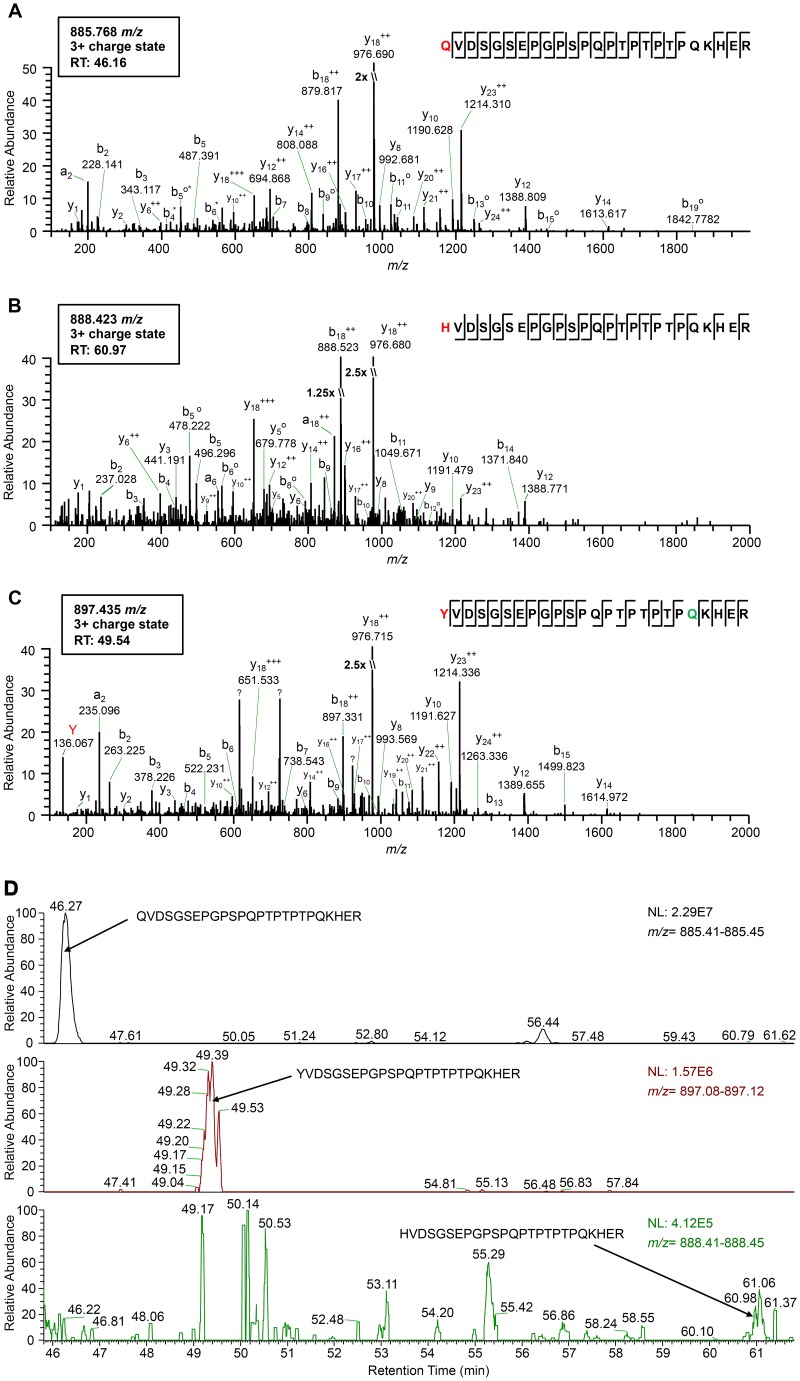
FIG 1.
High-resolution mass spectrometry identifies the amino acid residue incorporated at the CP amber stop codon position during readthrough. (A to C) Tandem mass spectra (MS2) of tryptic peptides spanning residues 209 to 233 in the PLRV RTP identified by affinity purification-MS analysis: K.Q209VDSGSEPGPSPQPTPTPTPQKHER.F (m/z 885.768) (A), K.H209VDSGSEPGPSPQPTPTPTPQKHER.F (m/z 888.423) (B), and K.Y209VDSGSEPGPSPQPTPTPTPQKHER.F (m/z 897.435) (C). Sequences show fragmentation along the peptide backbone and indicate the identity of residue 209 (red) and other ions that were used in peptide identification. For simplicity, only a representative amount of fragment ions in spectra are labeled. The ion peak highlighted in red indicates an immonium ion corresponding to the identity of a tyrosine residue at position 209. The residue highlighted in green indicates deamidation. RT, peptide retention time; ++, doubly charged ion; o, loss of H2O; *, loss of NH3; ?, contaminating fragment ions most likely from a coeluting peptide. (D) Relative abundances of the K.X209VDSGSEPGPSPQPTPTPTPQKHER.F peptide isoforms identified in the same PLRV affinity purification from locally infected N. benthamiana. Extracted MS1 chromatograms for precursor ions with m/z values of 885.41 to 885.45 (top), 897.08 to 897.12 (middle), and 888.41 to 888.45 (low) detected between 45.80 and 61.80 min (retention time) are shown. Arrows indicate the MS1 peak corresponding to peptide K.Q209VDSGSEPGPSPQPTPTPTPQKHER.F (retention time, 46.27 min) (A), K.Y209VDSGSEPGPSPQPTPTPTPQKHER.F (retention time, 49.39 min) (B), and K.H209VDSGSEPGPSPQPTPTPTPQKHER.F (retention time, 60.96 min) (C). The area under each peak is equal to the relative abundance of each peptide ion, with 100 on the y axis equaling the normalization (NL) value given in each panel.