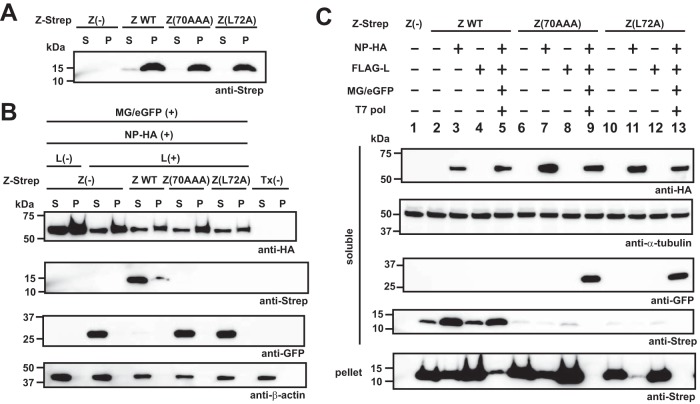
FIG 4.
Effect of L72A mutation on Z protein stability in the presence of an active vRNP. (A) Solubility of WT and mutant Z proteins. 293T cells seeded in a 12-well plate were transfected with plasmids expressing Strep-tagged WT or the indicated mutant Z proteins. At 72 h posttransfection, the transfected cells were lysed with PD lysis buffer (+) and soluble (S) and insoluble fractions separated by centrifugation at 21,130 × g at 4°C for 10 min. Pellet containing the insoluble fraction (P) was lysed with 2× SDS loading buffer. Z protein levels in the S and P fractions were analyzed by Western blotting. (B and C) Expression of mutant Z proteins in the presence of an active vRNP. 293T cells seeded in a 12-well plate were transfected with pT7-MG/eGFP (MG/eGFP) and pC-T7pol (T7 pol), pC-NP-HA (NP-HA), and either pC-L (L) or pC-FALG-L (FLAG-L) together with or without a plasmid expressing WT or the indicated mutant Z proteins or remained untransfected [Tx(−)]. Plus and minus signs indicate plasmid presence and absence in the transfection mix. At 72 h posttransfection, protein levels in the S and P fractions were analyzed by Western blotting.