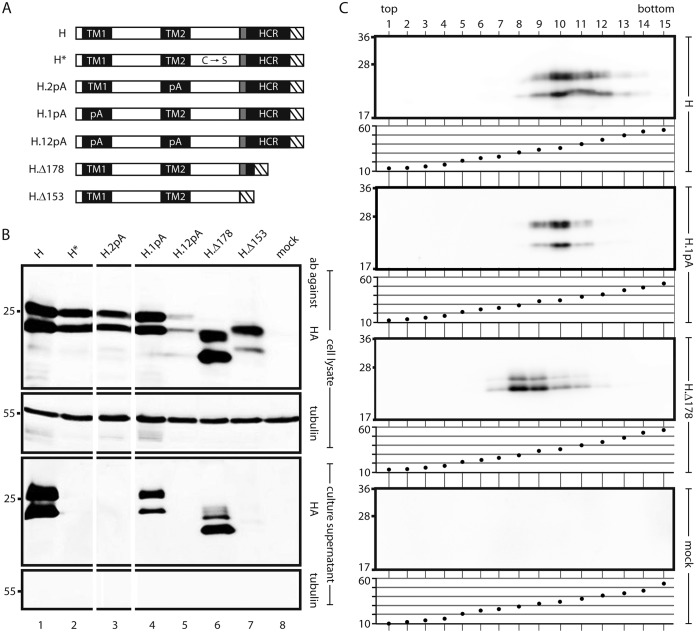
FIG 3.
Influence of mutations in transmembrane domains of S on SVP formation. (A) Map of S derivatives. Filled rectangles, transmembrane domains; shaded box, putative amphipathic helix; hatched box, HA tag. C → S, point mutations of all 8 cysteine residues in the LL to serine residues; 1pA, replacement of the central 11 aa of TM1 with alanine residues; 2pA, replacement of the central 13 aa of TM2 with alanine residues; Δ178 and Δ153, C-terminal deletions (the number indicates the position of the stop codon). (B) Western blots of cell lysates (upper two panels) and culture supernatants (lower two panels) stained with the indicated antibodies (ab). The positions of molecular size markers (in kilodaltons) are shown on the left. The 1pA mutation and the Δ178 truncation were compatible with secretion. (C) SVP formation by secretion-competent mutants. Culture supernatants of cells expressing the indicated constructs were sedimented through a sucrose gradient. For each construct, proteins were detected in gradient fractions by Western blotting using an HA antibody (upper panel) (the positions of molecular size markers [in kilodaltons] are shown on the left), and the sucrose concentrations (percentages [wt/wt]) of the fractions were measured (lower panel).