FIG 4.
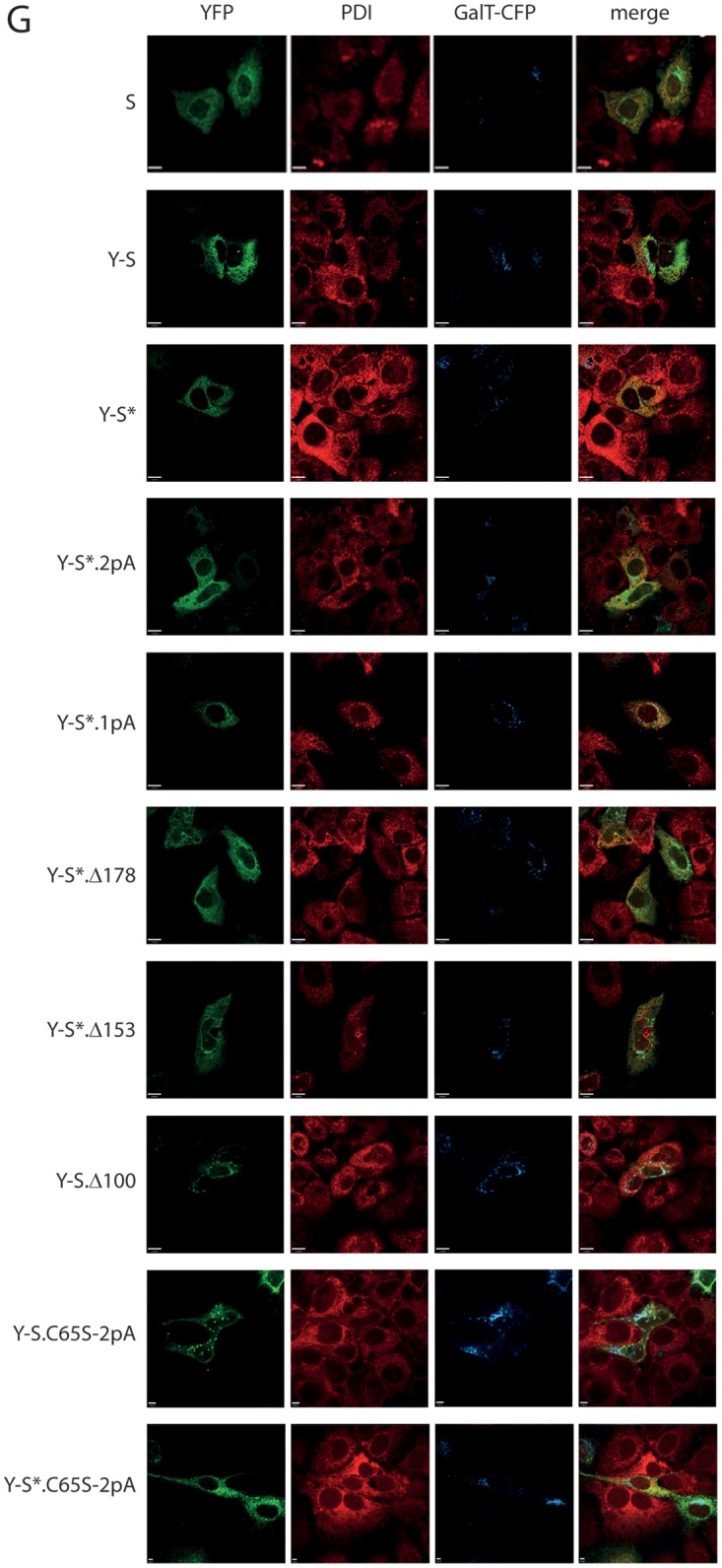
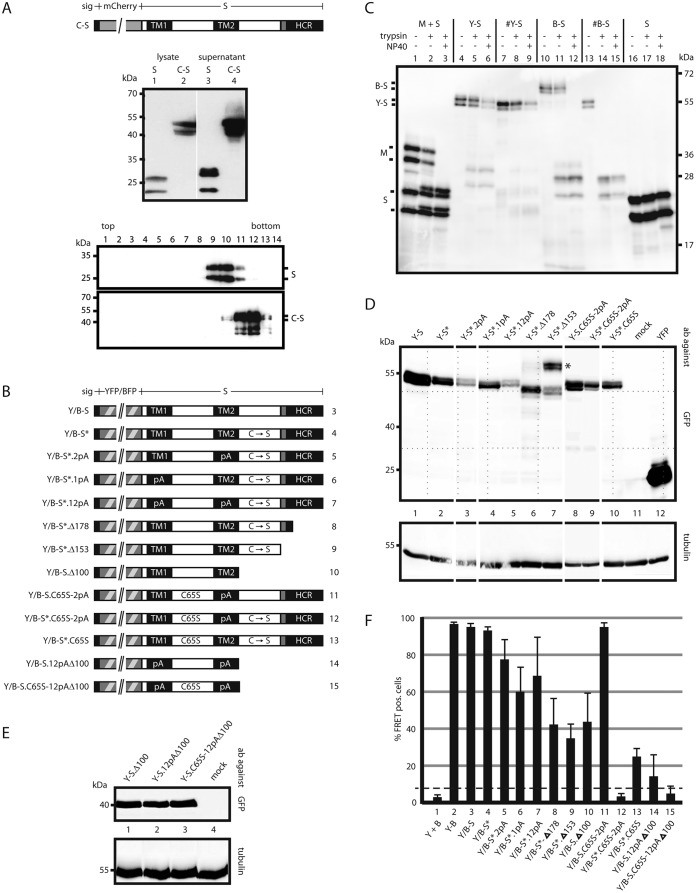
Influence of mutations in S on oligomerization. (A) A fluorescent derivative of S competent for SVP formation. (Top) Map of the fusion protein C-S carrying an N-terminal secretion signal (sig). (Center) Western blot of lysates and culture supernatants of cells expressing WT S or C-S stained with a monoclonal anti-HBs antibody. (Bottom) Western blot of fractions from a sucrose gradient after rate zonal centrifugation. (B) Map of constructs. All constructs carry a YFP or BFP moiety (hatched box) at the N terminus preceded by a secretion signal (small filled box). TM1 and TM2, transmembrane domains; HCR, hydrophobic C-terminal region; shaded box, putative amphipathic helix; pA, substitution of the central 11 aa (in TM1) or the central 13 aa (in TM2) with alanine residues; C → S, substitution of all eight cysteine residues in the LL with serine residues; C65S, replacement of cysteine 65 by serine. The numbers on the right correspond to lanes in panel F. (C) Transmembrane topologies of the Y-S and B-S chimeras. Microsomes from cells expressing the indicated proteins were treated with trypsin in the absence or presence of the mild detergent NP40. The S protein was resistant to trypsin cleavage. The pre-S2 domain of the M protein was cleaved only when microsomes were opened (lane 3), as expected (28). B-S showed a phenotype equivalent to that of M. Y-S was not efficiently cleaved. #Y-S and #B-S are similar to Y-S and B-S, respectively, but lack the N-terminal secretion signal. (D and E) Western blots of lysates from cells expressing the indicated constructs. Blots were stained with anti-GFP (cross-reacting with YFP) (top) or with anti-tubulin as a loading control (bottom). Blots in panel E were developed 5 times longer than those in panel D. The positions of molecular size markers are indicated on the left. (F) FACS-FRET signals from cells expressing the indicated YFP/BFP pairs. Y + B, coexpression of YFP and BFP; Y-B, fused YFP-BFP chimera. The dashed line indicates the background threshold. (G) Intracellular distribution of Y-S derivatives. Cells expressing the indicated constructs (autofluorescence) (green) and a fluorescent version of the Golgi enzyme GalT (GalT-CFP) (blue) were stained with an antibody against the ER-resident protein PDI (red) and were analyzed by immunofluorescence. The WT S protein was stained with polyclonal anti-HBs and a second fluorescent antibody. The bars indicate a distance of 12 μm. All constructs show a diffuse pattern in the ER and a punctate pattern in the Golgi complex, like the WT S protein.