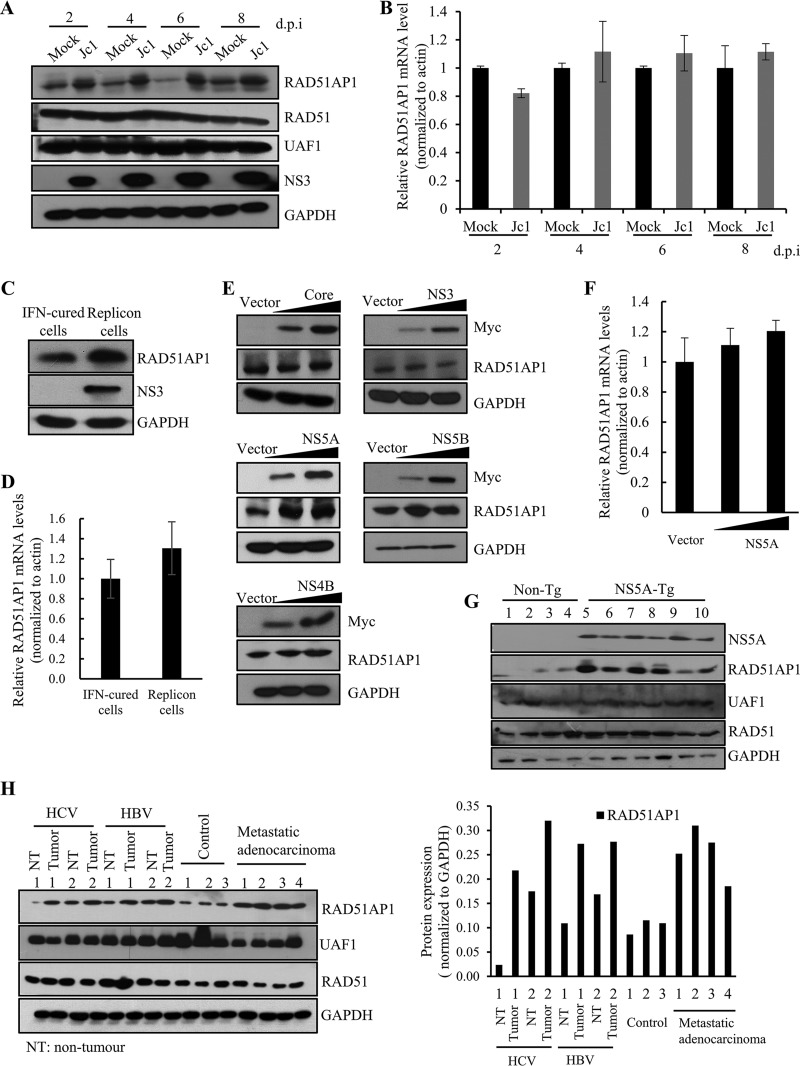
FIG 2.
HCV infection increases the RAD51AP1 protein expression level through NS5A. (A) Huh7.5 cells were either mock infected or infected with Jc1. Total cell lysates harvested at various time points were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. d.p.i, days postinfection. (B) RAD51AP1 mRNA levels for the set of experiments for panel A were analyzed by qRT-PCR. (C) Total cell lysates harvested from either IFN-cured Huh7 cells or Huh7 cells harboring an HCV subgenomic replicon (genotype 1b) were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (D) RAD51AP1 mRNA levels in IFN-cured cells and HCV replicon cells were determined by qRT-PCR. (E) Huh7 cells were transiently transfected with either vector or increasing amounts of Myc-tagged core, NS3, NS4B, NS5A, or NS5B plasmid. At 36 h posttransfection, protein levels were immunoblotted by use of the indicated antibodies. (F) Huh7 cells were transiently transfected with either vector or increasing amounts of Myc-tagged NS5A plasmid. RAD51AP1 mRNA levels were analyzed by qRT-PCR. Experiments were performed in triplicate. (G) Liver tissues of either nontransgenic (n = 4) or NS5A-transgenic (n = 5) mice were homogenized and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (H) (Left) Human liver tissues isolated from either control or various patients were homogenized and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (Right) RAD51AP1 expression levels were quantified after normalization to the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) level.