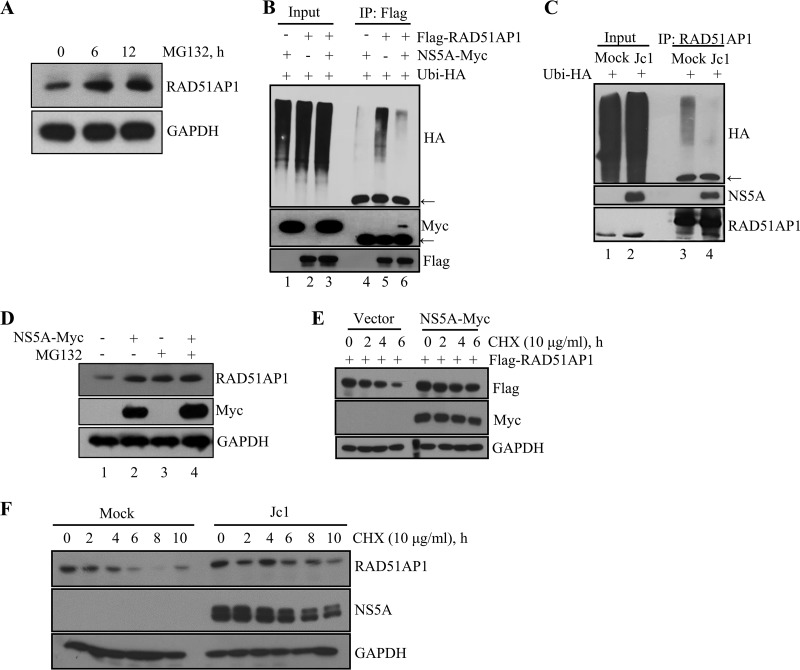
FIG 3.
HCV NS5A protects RAD51AP1 from ubiquitin-dependent proteasomal degradation. (A) Huh7 cells were treated with 20 μM MG132 for the indicated time points, and protein levels were determined by immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies. (B) HEK293T cells were cotransfected with the indicated combinations of plasmids. At 36 h posttransfection, total cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an anti-Flag antibody, and bound proteins were immunoblotted with an anti-HA antibody. Arrows indicate the position of the heavy chain. (C) Huh7 cells that were either mock infected or infected with Jc1 for 48 h were transfected with HA-tagged ubiquitin. At 36 h posttransfection, total cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an anti-RAD51AP1 antibody, and bound proteins were immunoblotted with an anti-HA antibody. (D) Huh7 cells were transfected with either vector or a Myc-tagged NS5A expression plasmid. At 36 h posttransfection, cells were left untreated or treated with 20 μM MG132 for 6 h, and protein levels were determined by immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies. (E) HEK293 cells were cotransfected with the indicated combinations of plasmids. At 30 h posttransfection, cells were treated with 10 μg/ml of CHX for the indicated time points, and protein levels were determined by immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies. (F) Huh7 cells that were either mock infected or infected with Jc1 for 48 h were treated with 10 μg/ml of CHX for the indicated time points, and protein levels were determined by immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies.