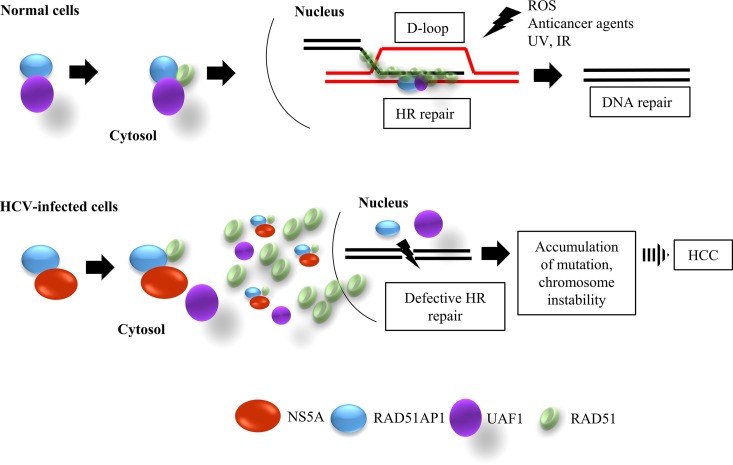
FIG 9.
Proposed model for defective DNA repair mechanism in HCV-infected cells. In normal cells, UAF1 forms a complex with RAD51AP1 and cooperates with RAD51 to promote the assembly of the synaptic complex, a critical nucleoprotein intermediate in HR repair. RAD51/RAD51AP1/UAF1 is indispensable for genome maintenance and against the DNA damage caused by exogenous agents. In HCV-infected cells, NS5A interacts with RAD51AP1, and thus RAD51AP1-UAF1 interaction is inhibited. This in turn disturbs the trimeric complex of RAD51, RAD51AP1, and UAF1 and leads to the accumulation of RAD51 in the cytoplasm. Consequently, DNA repair is compromised in HCV-infected cells. Defective DNA repair results in an increased mutation frequency and a consequent high incidence of HCC. IR, ionizing radiation.