Figure 1.
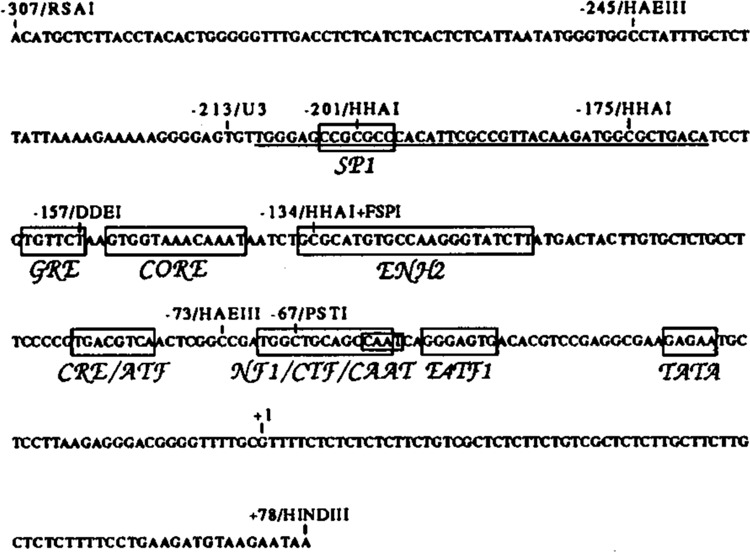
Nucleotide sequence of the IAP LTR from the pIAP.l sequence (Howe and Overton, 1986). Shown above the sequence are various restriction enzymes sites, the beginning of the LTR (−213), and the transcriptional start site (+1). Boxed with abbreviations below the sequence are transcriptional elements, most of which were identified on the basis of homology to known transcriptional elements, including: an Sp1 binding site (Sp1) (Briggs et al., 1986); a glucocorticoid response element (Scheidereit and Beato, 1984); an SV40 core enhancer sequence (Weiher et al., 1983); a cAMP response element or the homologous ATF binding site (CRE/ATF) (Montminy et al., 1986; Lin and Green, 1988); a nuclear factor 1 or the homologous CCAAT transcription factor binding site (NF1/CTF/CAAT) (Jones et al., 1987); an E4TF1 binding site (E4TF1) (Watanabe et al., 1988); and a non-consensus TATA box. Also boxed is an enhancer element identified on the basis of function that binds protein factor EBP80 (Falzon and Kuff, 1990). The underlined sequence represents the DNAse I footprinted region from −210 to −168 (see Fig. 4).
