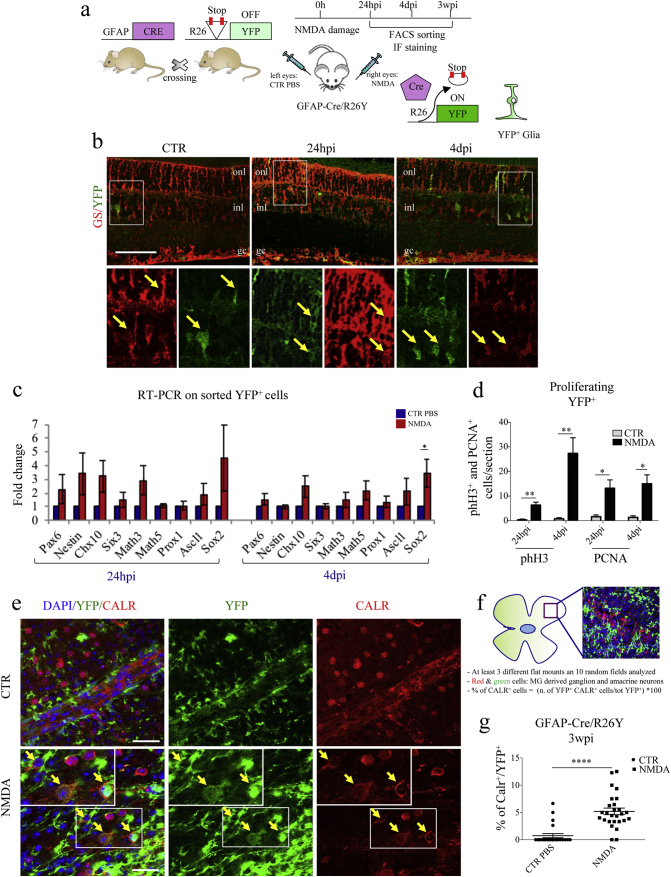
Fig. 1.
Müller glial cells (MGCs) undergo reprogramming and differentiate into CALR+ cells following NMDA-damage. (a) Experimental scheme. We used transgenic GFAP-Cre/R26Y mice. In these mice, ubiquitous expression of YFP is impeded by the presence of a floxed-STOP codon, which can be excised by Cre recombinase. Expression of Cre recombinase is driven by the glial-specific GFAP promoter. As a consequence, the YFP reporter allows to trace glial cells. We injected NMDA in the right eyes to induce retinal degeneration. Left eyes were injected with PBS, as controls. We characterized YFP+ cells at various time-points post-injection. (b) Representative immunostaining of retinal sections harvested from GFAP-Cre/R26Y mice sacrificed 24 hpi and 4 dpi. Higher magnification images (from the areas enclosed by the white boxes) are shown in the bottom panel. YFP+ cells (green) are also positive for GS (red), a well-known glial marker (onl, outer nuclear layer; inl, inner nuclear layer; gc, ganglion cells layer). Scale bar: 100 μm. (c) RT-PCR expression analysis of neural stem cell and retinal progenitor genes using total RNA harvested from FACS-sorted YFP+ cells of either PBS-treated (CTR) or NMDA-damaged (NMDA) retinae of GFAP-Cre/R26Y mice, 24 hpi and 4 dpi. Transcript levels are expressed as fold-changes relative to YFP+ cells sorted from PBS-injected retinae. Data are represented as mean ± S.E.M. (n = 4). Statistical analysis is based on unpaired Student's t-test (24 hpi: Pax6, p = 0.3533ns;Nestin, p = 0.1704ns; Chx10, p = 0.1009ns; Six3, p = 0.3896ns; Math3, p = 0.1157ns; Math5, p = 0.5200ns; Prox1, p = 0.8599ns; Ascl1, p = 0.3695ns; Sox2, p = 0.2774ns; 4 dpi: Pax6, p = 0.2357ns; Nestin, p = 0.3592ns; Chx10, p = 0.0771ns; Six3, p = 0.8952ns; Math3, p = 0.4317ns; Math5, p = 0.1218ns; Prox1, p = 0.3917ns; Ascl1, p = 0.2790ns; Sox2, p = 0.0378⁎). (d) Quantification of proliferating MGCs. Results are presented as number of counted PCNA+/YFP+ and phH3+/YFP+ cells per section, 24 hpi and 4 dpi, both for PBS-treated (CTR) and NMDA-damaged (NMDA) retinae. Data are represented as mean ± S.E.M. (n = 3). Statistical analysis is based on unpaired Student's t-test (phH3: 24 hpi, p = 0.0086⁎⁎; 4 dpi, p = 0.0042⁎⁎; PCNA: 24 hpi, p = 0.0103⁎; 4 dpi, p = 0.0203⁎). (e) Immunostaining of retinal flat mounts from GFAP-Cre/R26Y mice sacrificed 3 weeks post-injection. Representative fields from PBS-injected (CTR) and NMDA-damaged (NMDA) retinae. YFP+ cells (green) differentiating into CALR+ cells (red) are indicated by yellow arrows. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 20 μm. (f) Schematic representation of the method used for counting marker-positive cells in retinal flat mounts. GFAP-Cre/R26Y mice were used for these experiments. YFP+ and YFP+/CALR+ cells were counted in 10 random fields from at least three different retinal flat mounts for each treatment group. (g) Percentages of YFP+ cells expressing CALR, 3 wpi. Cells were counted in 6–10 random fields for each flat mount harvested from either PBS-injected (CTR) and damaged (NMDA) retinae. Data are represented as mean ± S.E.M. (n = 3). Statistical analysis is based on unpaired Student's t-test (p < 0.0001⁎⁎⁎⁎).