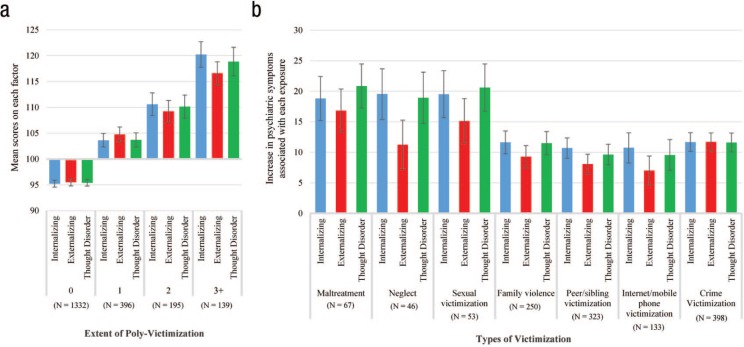
Fig. 1.
Associations between adolescent victimization and early-adult psychopathology, divided into its constituent symptom spectra (internalizing, externalizing, and thought disorders). (a) Mean scores on internalizing, externalizing, and thought disorders (from the correlated-factors model) at age 18 for Environmental Risk Longitudinal Twin Study (E-Risk) members exposed to 0, 1, 2, or 3+ types of severe adolescent victimization. All factor scores are scaled to a sample mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15. (b) Estimates reflect coefficients from separate linear mixed models, which control for clustering by family. These coefficients represent the average difference in internalizing, externalizing, and thought disorder factor scores (from the correlated-factors model) at age 18 between exposed and nonexposed E-Risk members in standardized units, where 15 points equals 1 standard deviation. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals.