Figure 5.
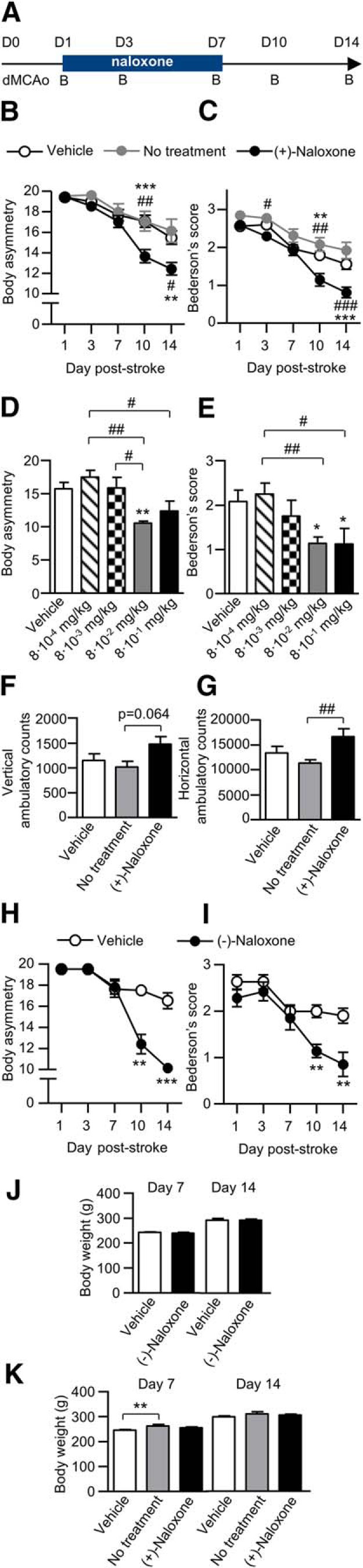
Post-stroke intranasal administration of naloxone enantiomers promotes functional recovery. A, Experimental timeline. Intranasal naloxone (or vehicle) was administered twice daily for 7 d post-stroke. D1–D14, post-stroke days 1–14; B, behavioral assay. B, C, Effects of (+)-naloxone (0.32 mg/kg; n = 27), vehicle (n = 25), and no treatment (n = 13) on body asymmetry (B) and Bederson’s neurologic score test (C). **, p < 0.01 and ***, p < 0.001 indicate post hoc comparison between (+)-naloxone and vehicle groups, and #, p < 0.05, ##, p < 0.01, and ###, p < 0.001 indicate post hoc analysis between (+)-naloxone and no-treatment groups with Mann–Whitney U test after Kruskal–Wallis test. D, E, Effects of different doses of (+)-naloxone, 0.0008 mg/kg (n = 8), 0.008 mg/kg (n = 8), 0.08 mg/kg (n = 7), and 0.8 mg/kg (n = 8), compared to vehicle (n = 11) on day 14 post-stroke on body asymmetry (D) and Bederson’s neurologic score test (E). *, p < 0.05 and **, p < 0.01 indicate pairwise comparison with vehicle; #, p < 0.05 and ##, p < 0.01 indicate pairwise comparison with other (+)-naloxone doses with Mann–Whitney U test after Kruskal–Wallis test. F, G, Effects of (+)-naloxone (0.32 mg/kg; n = 16), vehicle (n = 16), and no treatment (n = 13) on vertical (F) and horizontal (G) activity measured for 24 h on day 14. ##, p < 0.01, Mann–Whitney U test after Kruskal–Wallis test. H–J, Effects of (–)-naloxone (0.32 mg/kg; n = 7) and vehicle (n = 11) on body asymmetry test (H), Bederson’s neurologic score test (I), and body weight (J). **, p < 0.01 and ***, p < 0.001 indicate comparison with vehicle group with Mann–Whitney U test. K, Effects of (+)-naloxone (0.32 mg/kg, n = 27), vehicle (n = 25), and no treatment (n = 13) on body weight on days 7 and 14 post-stroke. **, p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA, Bonferroni’s post hoc test. The data represent mean ± SEM.
