FIG 3.
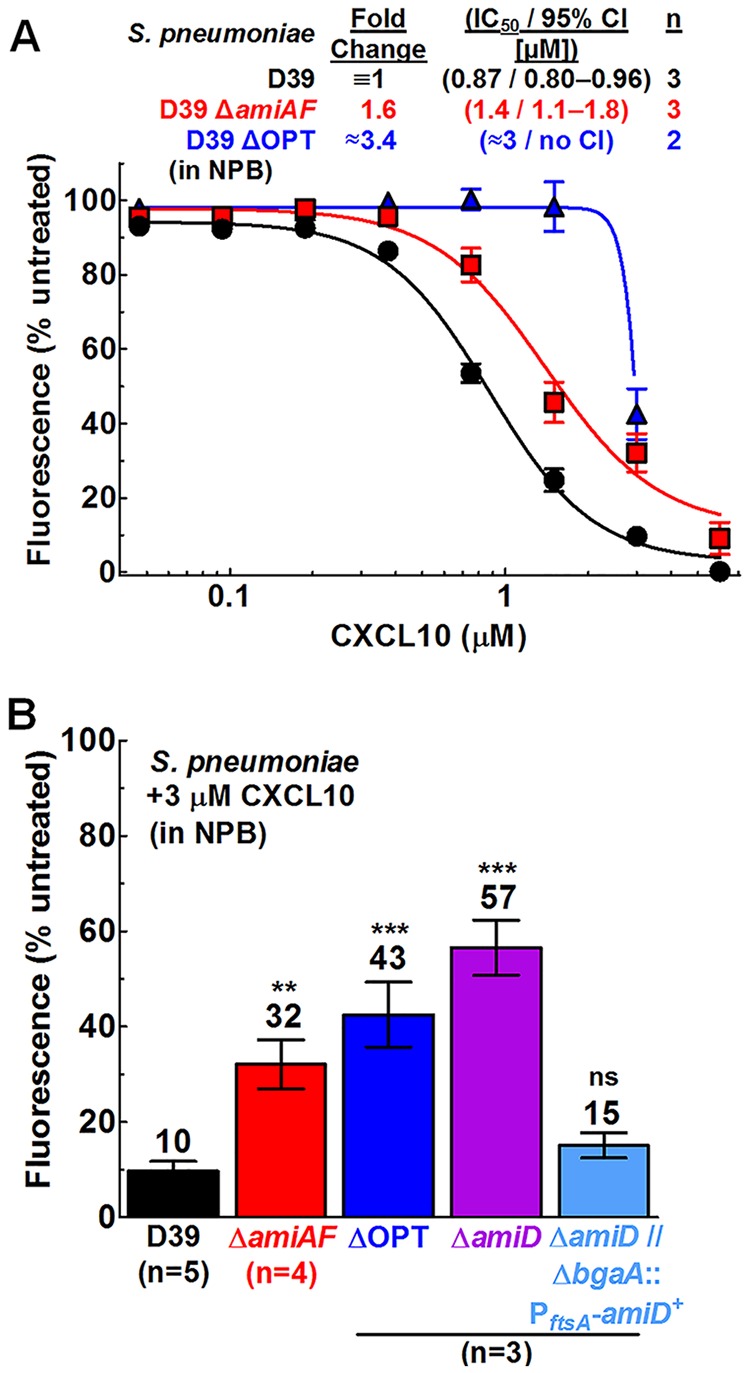
S. pneumoniae D39 ΔamiA-F, ΔamiD, and ΔOPT mutants show resistance to CXCL10 in NPB relative to the wild-type strain, and complementation of the ΔamiD mutant by an ectopic amiD+ strain restores CXCL10 sensitivity to wild-type levels. The sensitivity to CXCL10 in NPB was determined using a fluorescence-based antimicrobial assay (described in Materials and Methods). (A) S. pneumoniae D39 (IU1690), ΔamiA-F (ΔamiAF) (IU11759), and ΔOPT (IU11919). (B) The strains described above as well as the ΔamiD mutant (IU14488) and the ΔamiD ΔbgaA::PftsA-amiD+ mutant (IU14510) were treated with 3 μM CXCL10. Each data point or bar represents the mean ± SEM (where not visible, error bars are smaller than the symbol). “n” indicates the number of biologically independent replicates, each with duplicate reactions. For the titration experiments described for panel A, dose-response curves were fitted to pooled data in GraphPad Prism, using the “log of inhibitor versus response-variable slope” function. For the complementation experiments described for panel B, statistical significance relative to S. pneumoniae D39 was determined using the Mann-Whitney U test. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ns, not significant.
