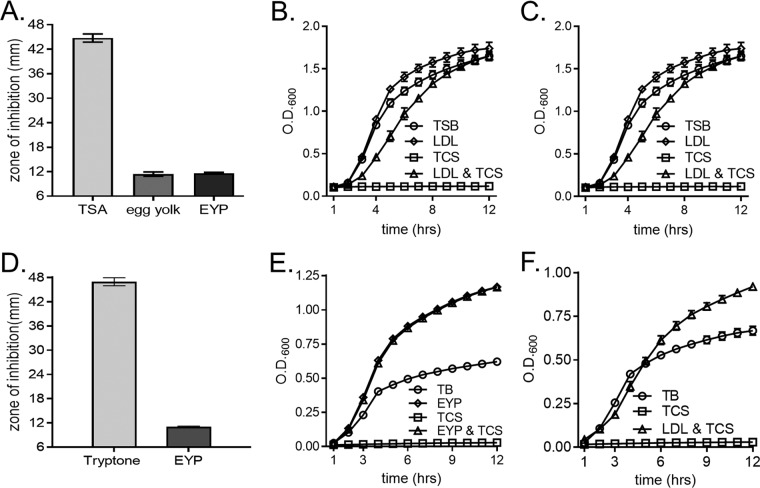
FIG 1.
Lipoprotein particles protect S. aureus from FASII inhibition by triclosan. (A) S. aureus was plated as a lawn on tryptic soy agar (TSA) with the following supplements to determine triclosan sensitivity by Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion assays: no supplementation, 1% chicken egg yolk, and 1% chicken egg yolk plasma (EYP). The mean diameter of the zone of inhibition from four independent experiments is shown. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. (B) The growth of S. aureus was monitored over time by measurement of the optical density (OD) in TSB under the following conditions: untreated, 1% EYP, 1 μM triclosan (TCS), or 1 μM triclosan with 1% EYP. The mean from six independent experiments is shown. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. (C) The growth of S. aureus was monitored over time by measurement of the OD in TSB under the following conditions: untreated, 0.34 μg/μl purified human LDL, 1 μM triclosan, or 1 μM triclosan with 0.34 μg/μl purified human LDL. (D) S. aureus was plated as a lawn on 1% tryptone agar with or without EYP for Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion assays to determine triclosan sensitivity, as described in the legend to panel A. The mean diameter of the zone of inhibition from four independent experiments is shown. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. (E) The growth of S. aureus was monitored over time by measurement of the OD in 1% tryptone broth under the following conditions: untreated, 1% EYP, 1 μM triclosan, or 1 μM triclosan with 1% EYP. The mean from four independent experiments is shown. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. (F) The growth of S. aureus was monitored over time by measurement of the OD in 1% tryptone broth under the following conditions: untreated, 1 μM triclosan, or 1 μM triclosan with 0.34 μg/μl purified human LDL. The mean from four independent experiments is shown. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean.