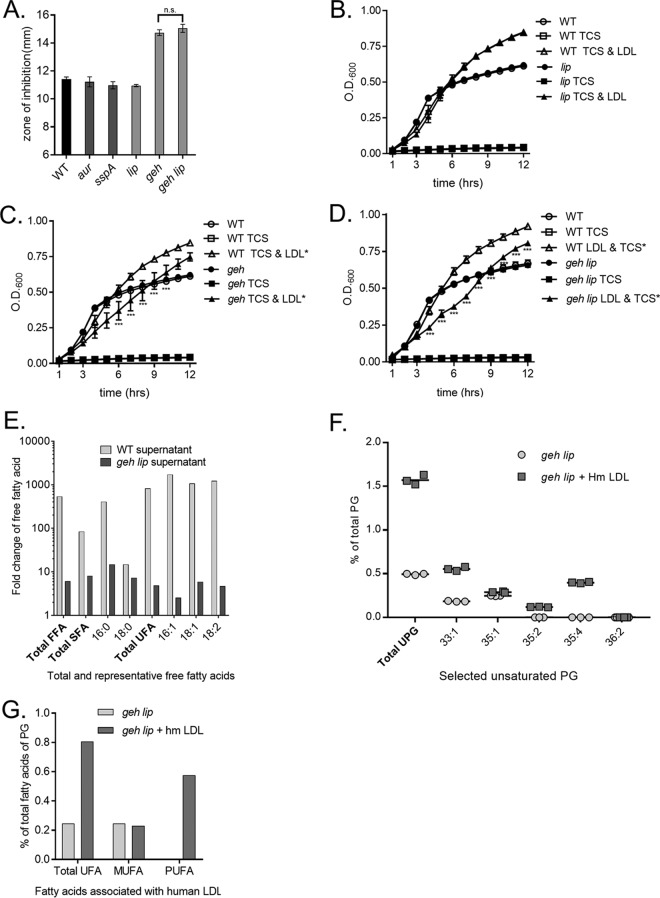
FIG 3.
The S. aureus lipase, encoded by geh, is required for full triclosan protection by lipoprotein particles. (A) The WT and protease (aur and sspA) and lipase (lip, geh, and lip geh) mutants were plated from overnight cultures as a lawn on 1% tryptone agar with or without 1% EYP. A triclosan-impregnated disk was placed on top of the agar. The mean diameter of the zone of inhibition from four independent experiments is shown. All error bars represent the standard error of the mean. (B to D) The growth of the WT and an isogenic geh transposon mutant (B), an isogenic lip transposon mutant (C), and an isogenic geh lip transposon mutant (D) was monitored over time by determination of the optical density (OD). Cells were grown in 1% tryptone broth under the following conditions: untreated, 1 μM triclosan (TCS), or 1 μM triclosan with 0.34 μg/μl purified human LDL. The mean results from four independent experiments are shown. ***, P < 0.005 by two-way ANOVA between the WT plus triclosan and LDL versus the geh or geh lip mutant plus triclosan and LDL; n.s., not statistically significant. All error bars represent the standard error of the mean. (E) The WT and the geh lip double mutant supernatants were incubated with human LDLs in triplicate. Free fatty acids (FFA) were detected by direct-infusion high-resolution/accurate mass spectrometry and tandem mass spectrometry, and the fold change calculated was based on the normalized number of ions per milligram. The fold change represents the amount of free fatty acids present in supernatant-treated samples compared to the amount of free fatty acids in the LDL preparation diluted in 1% tryptone broth. (F) Percentage of unsaturated PG (UPG) in comparison to the amount of total membrane PG of S. aureus grown in the presence or absence of human LDLs. (G) Unsaturated fatty acid profile of membrane PG of S. aureus grown with or without human LDLs plotted as a percentage of the amount of total PG fatty acids. SFA, UFA, MUFA, and PUFA, saturated, unsaturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fatty acids, respectively.